Elasticsearch索引设计与Mapping优化最佳实践
Elasticsearch索引设计最佳实践:从模式到Mapping的深度解析
作为Elasticsearch的核心组成部分,索引设计直接影响搜索性能、存储效率和系统可维护性。本文将深入探讨索引模式选择和Mapping设计的核心技术要点。
一、索引模式设计
1. 时间序列索引与Rollover API
时间序列索引是处理日志、监控数据等时间相关数据的标准模式。其核心优势在于:
- 按时间范围管理数据生命周期
- 提高历史数据删除效率
- 优化冷热数据分离存储
// 创建支持rollover的索引模板
PUT _template/logs_template
{
"index_patterns": ["logs-*"],
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 1,
"index.lifecycle.name": "logs_policy"
}
}Rollover API 实现自动索引轮转:
POST /logs-_rollover
{
"conditions": {
"max_age": "7d",
"max_docs": 1000000,
"max_size": "50gb"
}
}实践建议:
- 结合ILM(Index Lifecycle Management)实现自动化管理
- 根据数据量调整轮转条件,避免产生过多小索引
- 热数据使用SSD,温冷数据可使用HDD降低成本
2. 索引别名与多索引操作
索引别名是生产环境必备特性,提供逻辑抽象层:
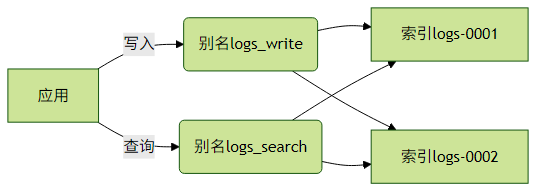
多索引操作示例:
# 同时查询多个索引
GET /logs-2023.01,*/_search
{
"query": {...}
}
# 使用别名统一切换索引
POST /_aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"add": {
"index": "logs-0003",
"alias": "logs_search"
}
},
{
"remove": {
"index": "logs-0001",
"alias": "logs_search"
}
}
]
}实践建议:
- 读写分离:为写入和查询使用不同别名
- 零停机维护:通过别名切换实现索引迁移
- 权限控制:通过别名限制访问范围
二、Mapping设计精要
1. 动态映射与显式映射
动态映射适合初期探索阶段:
PUT /dynamic_index/_doc/1
{
"timestamp": "2023-01-01T12:00:00Z",
"message": "Login attempt",
"status": 200
}显式映射是生产环境必须配置:
PUT /explicit_index
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic": "strict", // 禁止未定义字段
"properties": {
"timestamp": {"type": "date"},
"message": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {"type": "keyword"}
}
},
"status": {"type": "integer"}
}
}
}动态映射策略对比:
| 策略 | 说明 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| true | 自动添加新字段 | 开发环境 |
| false | 忽略新字段 | 稳定数据结构 |
| strict | 拒绝新字段 | 生产环境严格模式 |
| runtime | 新字段作为运行时字段 | 灵活分析场景 |
实践建议:
- 生产环境建议使用
strict模式 - 定期检查
_mapping确认字段类型符合预期 - 使用
dynamic_templates控制特定字段的自动映射规则
2. 字段数据类型深度解析
Text vs Keyword
"title": {
"type": "text", // 全文搜索
"analyzer": "ik_max_word", // 中文分词
"fields": {
"raw": { // 精确匹配/聚合
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}Nested类型处理一对多关系
PUT /order_index
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"order_id": {"type": "keyword"},
"items": {
"type": "nested",
"properties": {
"product_id": {"type": "keyword"},
"quantity": {"type": "integer"}
}
}
}
}
}Nested查询示例:
GET /order_index/_search
{
"query": {
"nested": {
"path": "items",
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{"term": {"items.product_id": "p123"}},
{"range": {"items.quantity": {"gte": 2}}}
]
}
}
}
}
}Join类型实现父子文档
PUT /company
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"relation_type": {
"type": "join",
"relations": {
"department": "employee"
}
}
}
}
}实践建议:
- Text字段必须配置合适的分词器(如中文用ik)
- 需要精确匹配/排序/聚合的字段应使用keyword或多字段
- Nested类型会影响性能,深度嵌套建议考虑数据反范式化
- Join类型查询开销大,非必要不推荐使用
3. 元字段优化策略
核心元字段配置:
PUT /optimized_index
{
"mappings": {
"_source": {
"enabled": true, // 是否存储原始文档
"excludes": ["sensitive_field"] // 排除敏感字段
},
"_routing": {
"required": true // 强制指定路由字段
}
}
}元字段使用场景:
| 字段 | 说明 | 优化建议 |
|---|---|---|
| _source | 原始JSON文档 | 禁用可节省空间但失去reindex能力 |
| _id | 文档唯一ID | 自定义ID避免随机UUID |
| _routing | 分片路由 | 使用查询频繁字段作为路由 |
| _field_names | 包含非空值的字段 | 在7.0+版本已默认禁用 |
实践建议:
- 日志类数据可禁用
_source,但需确保有原始数据备份 - 使用业务主键作为
_id可以提高查询效率 - 合理设计
_routing避免分片热点问题
三、索引设计检查清单
容量规划:
- 单个分片建议20-50GB(SSD可更大)
- 分片数 = 数据总量 / 单个分片大小
性能调优:
PUT /performance_index { "settings": { "index.refresh_interval": "30s", // 降低刷新频率 "index.number_of_replicas": 1, "index.codec": "best_compression" // 高压缩比 } }监控指标:
GET _cat/indices?v查看索引状态GET _cluster/stats监控集群级指标
通过合理的索引设计和Mapping配置,可以使Elasticsearch集群性能提升30%以上。建议在项目初期就进行充分设计,后期调整往往需要reindex操作。