Elasticsearch数据建模指南:关系型与非结构化处理
Elasticsearch数据建模实战:从关系型映射到非结构化处理
作为分布式搜索和分析引擎,Elasticsearch的数据建模与传统关系型数据库有着显著差异。本文将深入探讨两种典型场景下的建模方案:关系型数据映射和非结构化数据处理,帮助您构建高效的搜索系统。
一、关系型数据映射
1. Nested类型处理一对多关系
在关系型数据库中,我们常用外键关联处理一对多关系,而在Elasticsearch中,Nested类型是更自然的选择。当主文档包含对象数组且需要独立查询时,Nested类型能保持数组元素的独立性。
PUT /products
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": { "type": "text" },
"variants": {
"type": "nested",
"properties": {
"color": { "type": "keyword" },
"size": { "type": "keyword" },
"price": { "type": "double" }
}
}
}
}
}查询时使用专门的nested查询语法:
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"nested": {
"path": "variants",
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "term": { "variants.color": "red" } },
{ "range": { "variants.price": { "gte": 100 } } }
]
}
}
}
}
}实践建议:
- Nested文档数量不宜过多(通常不超过100个),否则影响性能
- 查询时尽量指定具体path减少计算量
- 考虑使用
include_in_parent参数在必要时将字段提升到父文档
2. Parent-Child模型适用场景
Parent-Child模型适合以下场景:
- 子文档数量大且更新频繁
- 需要独立查询子文档
- 父子文档有不同生命周期
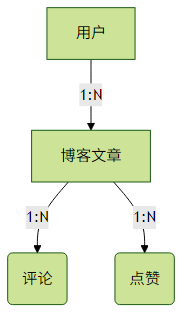
建立父子关系的mapping示例:
PUT /blogs
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": { "type": "text" },
"user_id": { "type": "keyword" },
"comments": {
"type": "join",
"relations": {
"post": "comment"
}
}
}
}
}性能对比:
| 特性 | Nested类型 | Parent-Child模型 |
|---|---|---|
| 查询性能 | 较快(同文档) | 较慢(跨文档join) |
| 更新开销 | 高(重建整个文档) | 低(只更新子文档) |
| 适用场景 | 少量关联数据 | 大量关联或频繁更新 |
实践建议:
- 父子文档应放在同一分片(需使用相同的routing值)
- 考虑使用
has_child和has_parent查询进行关联检索 - 对于读多写少场景,Nested类型通常是更好选择
二、非结构化数据处理
1. 全文检索与语义分析
Elasticsearch强大的文本处理能力来自其分析链(Analysis Chain):

典型的多语言分析器配置:
PUT /news
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"chinese_analyzer": {
"type": "custom",
"tokenizer": "ik_max_word",
"filter": ["lowercase"]
},
"english_analyzer": {
"type": "custom",
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": ["lowercase", "stemmer"]
}
}
}
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"cn_content": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "chinese_analyzer"
},
"en_content": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "english_analyzer"
}
}
}
}实践建议:
- 中文推荐使用IK Analyzer插件
- 英文考虑添加同义词过滤器(synonym)
测试分析效果可使用
_analyzeAPI:POST /news/_analyze { "analyzer": "chinese_analyzer", "text": "Elasticsearch是一款强大的搜索引擎" }
2. 多字段(Multi-fields)策略
多字段技术允许一个字段以不同方式索引,满足多种查询需求:
PUT /products
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"product_name": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "standard",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"stemmed": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "english"
},
"ngram": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ngram_analyzer"
}
}
}
}
}
}查询时指定字段后缀:
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"product_name.stemmed": "running"
}
}
}典型多字段组合:
| 主字段类型 | 子字段用途 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| text | keyword | 精确匹配、聚合 |
| text | 不同语言分析器 | 多语言支持 |
| text | ngram/edge_ngram | 输入提示 |
| keyword | wildcard | 通配符查询 |
| geo_point | geohash | 地理哈希聚合 |
实践建议:
- 主字段用于常规搜索,特殊需求使用子字段
- 监控字段数量,避免"字段爆炸"
- 考虑在索引模板中统一配置常用多字段模式
三、数据建模最佳实践
- 避免过度嵌套:嵌套层级不超过3层,复杂关联考虑应用层处理
- 区分热温数据:使用ILM(Index Lifecycle Management)自动转移旧数据
- 版本控制:通过
_version字段或外部版本控制处理并发更新 - 稀疏字段处理:对可选字段使用
null_value设置默认值 - 测试验证:使用
_validate/queryAPI验证查询性能
通过合理的数据建模,Elasticsearch可以高效处理从结构化到非结构化的各类数据场景,为应用提供灵活的搜索和分析能力。