Spring MVC与RESTful Web服务开发实战指南
Spring MVC与RESTful Web服务开发实战指南
一、Spring MVC核心架构
Spring MVC是Spring框架提供的Web应用开发模块,采用经典的MVC(Model-View-Controller)设计模式。
1. DispatcherServlet:前端控制器
DispatcherServlet是Spring MVC的核心,负责请求的分发和处理流程的协调。
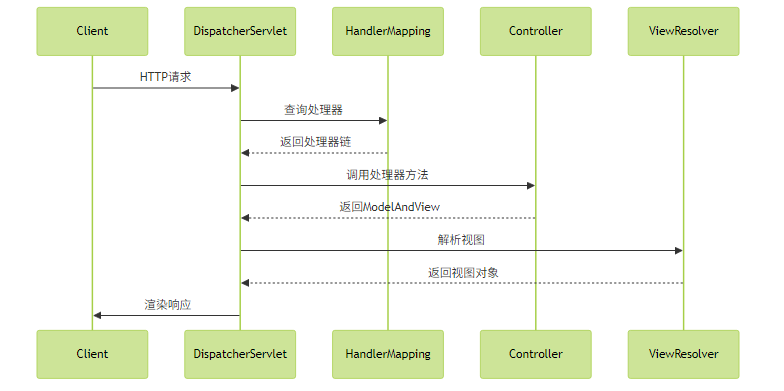
实践建议:
- 在web.xml中配置DispatcherServlet时,设置
load-on-startup为1确保应用启动时初始化 - 通过
<init-param>配置contextConfigLocation指定Spring配置文件位置
2. 控制器开发(@Controller)
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/products")
public class ProductController {
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String getProduct(@PathVariable Long id, Model model) {
Product product = productService.findById(id);
model.addAttribute("product", product);
return "productDetail";
}
}关键注解:
@Controller:标识类为控制器组件@RequestMapping:定义请求映射路径@GetMapping/@PostMapping:特定HTTP方法的映射
实践建议:
- 保持控制器简洁,业务逻辑应放在Service层
- 使用明确的URL命名规范(如RESTful风格)
- 避免在控制器中直接处理异常,使用
@ControllerAdvice统一处理
3. 视图解析机制
Spring MVC支持多种视图技术(JSP、Thymeleaf、FreeMarker等),通过ViewResolver实现解耦。
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Bean
public ViewResolver viewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver resolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
resolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/");
resolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return resolver;
}
}二、RESTful服务开发
1. @RestController与响应体处理
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/products")
public class ProductApiController {
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Product> getProduct(@PathVariable Long id) {
return productService.findById(id)
.map(ResponseEntity::ok)
.orElse(ResponseEntity.notFound().build());
}
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<Product> createProduct(@Valid @RequestBody Product product) {
Product saved = productService.save(product);
URI location = ServletUriComponentsBuilder.fromCurrentRequest()
.path("/{id}")
.buildAndExpand(saved.getId())
.toUri();
return ResponseEntity.created(location).body(saved);
}
}核心注解:
@RestController:组合了@Controller和@ResponseBody@RequestBody:将请求体反序列化为Java对象@ResponseBody:将方法返回值序列化为响应体
2. REST客户端(RestTemplate)
@Service
public class ProductClientService {
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
public ProductClientService(RestTemplateBuilder builder) {
this.restTemplate = builder.rootUri("https://api.example.com").build();
}
public Product getProduct(Long id) {
return restTemplate.getForObject("/products/{id}", Product.class, id);
}
public Product createProduct(Product product) {
return restTemplate.postForObject("/products", product, Product.class);
}
}实践建议:
- 使用RestTemplateBuilder创建RestTemplate实例
- 对于复杂场景,考虑使用WebClient(响应式)或Feign(声明式)
- 始终处理HTTP错误响应(使用ResponseEntity或异常处理)
三、Spring Security集成
1. 基础安全配置
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/public/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
.and()
.logout()
.logoutSuccessUrl("/")
.and()
.csrf().disable(); // 仅开发环境禁用,生产环境必须启用
}
}2. 方法级安全控制
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/orders")
public class OrderController {
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('USER')")
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Order> getOrder(@PathVariable Long id) {
// ...
}
@PreAuthorize("#userId == authentication.principal.id")
@GetMapping("/user/{userId}")
public List<Order> getUserOrders(@PathVariable Long userId) {
// ...
}
}安全最佳实践:
- 始终启用CSRF防护(表单提交和状态修改操作)
- 使用HTTPS保护敏感数据传输
- 实施适当的CORS策略
- 定期审计安全配置和依赖库
四、常见问题解决方案
问题1:日期格式处理
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {
DateTimeFormatterRegistrar registrar = new DateTimeFormatterRegistrar();
registrar.setUseIsoFormat(true);
registrar.registerFormatters(registry);
}
}问题2:全局异常处理
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(ResourceNotFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> handleNotFound(ResourceNotFoundException ex) {
ErrorResponse response = new ErrorResponse(
"NOT_FOUND",
ex.getMessage(),
Instant.now()
);
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND).body(response);
}
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> handleValidation(MethodArgumentNotValidException ex) {
List<String> errors = ex.getBindingResult()
.getFieldErrors()
.stream()
.map(FieldError::getDefaultMessage)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
ErrorResponse response = new ErrorResponse(
"VALIDATION_FAILED",
"Invalid request content",
Instant.now(),
errors
);
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(response);
}
}五、性能优化策略
控制器优化:
- 使用
@ResponseStatus替代ResponseEntity简化代码 - 对只读操作使用
@Cacheable缓存响应 - 避免在控制器中进行耗时操作
- 使用
视图渲染优化:
- 启用模板缓存(Thymeleaf/Freemarker)
- 使用静态资源版本控制(避免浏览器缓存问题)
安全优化:
- 限制HTTP方法(如
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers(HttpMethod.POST, "/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")) - 实施速率限制防止暴力破解
- 限制HTTP方法(如
REST优化:
- 实现ETag支持条件请求
- 使用分页返回大型数据集
- 支持内容协商(JSON/XML)
通过合理应用这些Spring MVC和REST开发技术,可以构建出结构清晰、安全可靠且高性能的Web应用程序。