Spring Boot高级特性解析:自动配置与Starter机制
Spring Boot高级特性深度解析
Spring Boot作为Spring生态中的"约定优于配置"实现,极大地简化了企业级应用的开发。本文将深入探讨Spring Boot的核心高级特性,帮助开发者掌握其精髓。
一、自动配置原理
Spring Boot的自动配置是其最显著的特性之一,它通过条件化配置减少了大量样板代码。
工作原理
graph TD
A[启动类@SpringBootApplication] --> B[启用自动配置@EnableAutoConfiguration]
B --> C[加载META-INF/spring/auto-configuration.imports]
C --> D[筛选有效的自动配置类]
D --> E[应用条件注解@Conditional]
E --> F[创建符合条件的Bean]自动配置的核心在于@Conditional系列注解,常见的有:
@ConditionalOnClass:类路径下存在指定类时生效@ConditionalOnMissingBean:容器中不存在指定Bean时生效@ConditionalOnProperty:配置属性满足条件时生效
实践建议:
- 通过
--debug参数启动应用可查看自动配置报告 - 自定义自动配置时,确保配置类在
META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports中注册
二、Starter依赖机制
Starters是一组预定义的依赖描述符,简化了依赖管理。
常用Starters示例
<!-- Web Starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Data JPA Starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>自定义Starter步骤:
- 创建
autoconfigure模块包含核心逻辑 - 创建
starter模块作为依赖入口 - 添加
META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports文件
三、Actuator监控
Actuator提供了生产级监控端点,可通过HTTP或JMX访问。
关键端点
| 端点 | 描述 | 默认启用 |
|---|---|---|
| /health | 应用健康状态 | 是 |
| /metrics | 应用指标数据 | 否 |
| /loggers | 查看和修改日志级别 | 否 |
| /prometheus | Prometheus格式的指标数据 | 否 |
安全配置示例:
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: health,info,metrics
endpoint:
health:
show-details: when_authorized四、外部化配置
Spring Boot支持多层级的外部配置源,优先级从高到低为:
- 命令行参数
- JNDI属性
- Java系统属性
- 操作系统环境变量
- 应用配置文件(application-{profile}.yml)
Profile特定配置示例:
# application-dev.yml
server:
port: 8081
# application-prod.yml
server:
port: 80
ssl:
enabled: true五、微服务支持
Spring Cloud核心组件
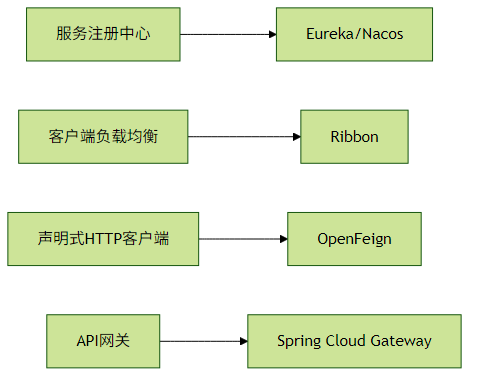
Feign客户端示例:
@FeignClient(name = "user-service")
public interface UserClient {
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
User getUser(@PathVariable Long id);
}六、响应式编程
WebFlux与传统MVC对比
| 特性 | WebMVC | WebFlux |
|---|---|---|
| 编程模型 | 命令式 | 响应式 |
| 线程模型 | 阻塞IO | 非阻塞IO |
| 并发能力 | 每个请求一个线程 | 少量线程处理所有请求 |
Reactor核心类型:
Mono:0-1个结果的异步序列Flux:0-N个结果的异步序列
示例:
@GetMapping("/users")
public Flux<User> getUsers() {
return userRepository.findAll();
}七、测试支持
测试切片注解
| 注解 | 测试目标 |
|---|---|
@WebMvcTest | 控制器层 |
@DataJpaTest | JPA仓库 |
@JsonTest | JSON序列化 |
@RestClientTest | REST客户端 |
集成测试示例:
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
class UserControllerTest {
@Autowired
private TestRestTemplate restTemplate;
@Test
void shouldReturnUser() {
ResponseEntity<User> response = restTemplate
.getForEntity("/users/1", User.class);
assertThat(response.getStatusCode()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.OK);
}
}实践建议
- 自动配置:理解自动配置原理有助于解决Bean冲突问题
- 监控:生产环境应合理暴露端点并做好安全防护
- 配置管理:敏感配置应使用Vault或配置中心管理
- 响应式:评估业务场景是否适合响应式编程,不要盲目使用
- 测试:合理使用测试切片提高测试效率
Spring Boot通过其"约定优于配置"的理念和丰富的功能集,极大地提升了开发效率。深入理解这些高级特性,能够帮助开发者构建更加健壮、高效的应用系统。