Spring最佳实践:设计模式与架构设计指南
Spring最佳实践:从设计模式到架构设计
Spring框架作为Java生态中最流行的开发框架,其最佳实践对于构建高质量应用至关重要。本文将深入探讨Spring应用中的设计模式应用、性能优化策略、常见问题解决方案以及架构设计考量。
一、设计模式在Spring中的应用
Spring框架本身就是设计模式的典范实现,理解这些模式有助于更好地使用框架。
1. 工厂模式 - BeanFactory
// 传统方式
UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
// Spring方式
@Autowired
private UserService userService;实践建议:
- 优先使用构造器注入,明确依赖关系
- 对于可选依赖,使用
@Autowired(required=false) - 考虑使用
@Qualifier解决多实现类的歧义问题
2. 代理模式 - AOP实现
@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public void logBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("Method called: " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
}
}实践建议:
- AOP适用于横切关注点:日志、事务、安全等
- 避免在切面中编写业务逻辑
- 注意切入点表达式的性能影响
3. 模板方法模式 - JdbcTemplate
public List<User> findAllUsers() {
return jdbcTemplate.query("SELECT * FROM users", (rs, rowNum) -> {
User user = new User();
user.setId(rs.getLong("id"));
user.setName(rs.getString("name"));
return user;
});
}实践建议:
- 使用NamedParameterJdbcTemplate提高SQL可读性
- 考虑使用RowMapper实现类代替匿名类
- 对于复杂查询,推荐使用JPA或MyBatis
二、性能优化策略
1. Bean初始化优化
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
@Lazy
public HeavyResource heavyResource() {
return new HeavyResource();
}
}优化建议:
- 合理使用
@Lazy延迟初始化 - 避免在
@PostConstruct中执行耗时操作 - 对于原型Bean,考虑使用对象池
2. 缓存优化
@Service
public class ProductService {
@Cacheable(value = "products", key = "#id")
public Product getProductById(Long id) {
// 数据库查询
}
}优化建议:
- 合理设置缓存过期时间
- 考虑使用多级缓存策略
- 对于热点数据,使用本地缓存+分布式缓存
3. 数据库访问优化
@Repository
public class UserRepository {
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public List<User> findAll() {
// 查询逻辑
}
}优化建议:
- 只读操作添加
readOnly=true - 合理设置事务隔离级别
- 批量操作使用
JdbcTemplate.batchUpdate()
三、常见问题解决方案
1. 循环依赖问题
// 解决方案1:使用setter注入代替构造器注入
@Service
public class ServiceA {
private ServiceB serviceB;
@Autowired
public void setServiceB(ServiceB serviceB) {
this.serviceB = serviceB;
}
}
// 解决方案2:使用@Lazy
@Service
public class ServiceA {
@Autowired
@Lazy
private ServiceB serviceB;
}最佳实践:
- 优先通过设计避免循环依赖
- 必须使用时选择setter注入
- 考虑重构为第三方服务
2. 事务失效场景
// 错误示例:同类方法调用
@Service
public class OrderService {
public void placeOrder(Order order) {
validateOrder(order); // 事务不会生效
// ...
}
@Transactional
public void validateOrder(Order order) {
// 验证逻辑
}
}解决方案:
- 将事务方法移到另一个Bean
- 使用AOP上下文
AopContext.currentProxy() - 使用编程式事务管理
3. 并发安全问题
@Service
@Scope(value = WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_REQUEST, proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS)
public class RequestScopedService {
// 每个请求独立实例
}最佳实践:
- 无状态Bean使用单例作用域
- 有状态Bean根据场景选择合适作用域
- 注意ThreadLocal的使用和清理
四、架构设计考量
1. 分层架构设计
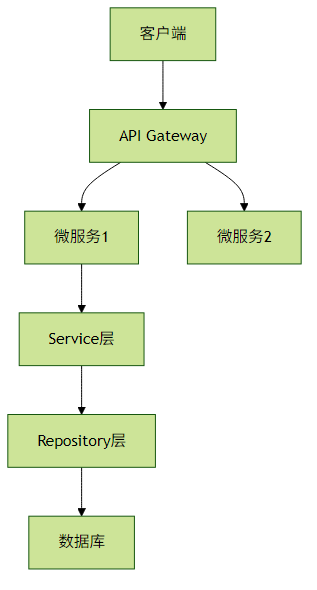
架构建议:
- 清晰定义各层职责
- 层间通过接口通信
- 避免跨层调用
2. 微服务设计
// Feign客户端示例
@FeignClient(name = "user-service", url = "${user.service.url}")
public interface UserServiceClient {
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
User getUserById(@PathVariable Long id);
}最佳实践:
- 服务划分遵循单一职责原则
- 接口设计考虑版本兼容性
- 实现熔断和降级机制
3. 响应式架构
@RestController
public class ReactiveUserController {
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
public Mono<User> getUserById(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userRepository.findById(id);
}
}迁移建议:
- 从非阻塞IO开始尝试
- 逐步替换阻塞组件
- 注意背压处理
五、总结
Spring最佳实践的核心在于:
- 合理使用设计模式:理解Spring背后的设计模式,写出更"Spring风格"的代码
- 性能优化有章法:从Bean生命周期到缓存策略,优化要有针对性
- 问题解决有套路:常见问题有标准解决方案,避免重复踩坑
- 架构设计有原则:根据业务规模选择合适架构,平衡灵活性与复杂度
实际项目中,这些实践往往需要根据具体场景灵活调整。建议建立适合自己团队的Spring开发规范,并通过Code Review保证实施。