Spring Security与OAuth2/JWT实战指南
Spring Security核心与OAuth2/JWT深度解析
一、Spring Security核心架构
1.1 认证(Authentication)与授权(Authorization)
认证是验证用户身份的过程,而授权是确定用户是否有权限执行特定操作。Spring Security通过这两个核心机制保护应用安全。
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("user").password("{noop}password").roles("USER")
.and()
.withUser("admin").password("{noop}admin").roles("ADMIN");
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.antMatchers("/user/**").hasAnyRole("USER", "ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin();
}
}实践建议:
- 生产环境务必使用加密密码存储(推荐BCryptPasswordEncoder)
- 遵循最小权限原则,只授予必要权限
- 敏感操作应增加二次认证
1.2 过滤器链与安全上下文
Spring Security基于Servlet过滤器链实现安全控制,核心过滤器包括:
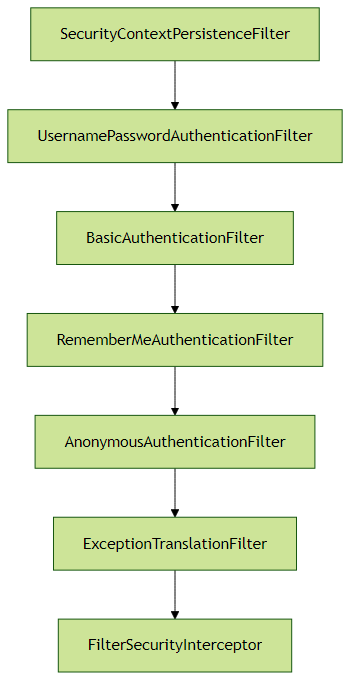
安全上下文(SecurityContext) 存储当前认证信息,通过SecurityContextHolder访问:
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
String username = authentication.getName();
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = authentication.getAuthorities();实践建议:
- 避免在业务代码中频繁访问SecurityContextHolder
- 异步场景下需手动传递安全上下文
- 自定义过滤器时注意执行顺序
二、OAuth2与JWT深度集成
2.1 资源服务器配置
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class ResourceServerConfig extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/api/public/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/api/private/**").authenticated()
.antMatchers("/api/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN");
}
@Override
public void configure(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources) {
resources.tokenServices(tokenServices());
}
@Bean
public TokenStore tokenStore() {
return new JwtTokenStore(jwtAccessTokenConverter());
}
@Bean
public JwtAccessTokenConverter jwtAccessTokenConverter() {
JwtAccessTokenConverter converter = new JwtAccessTokenConverter();
converter.setSigningKey("secret-key");
return converter;
}
}2.2 JWT令牌管理
JWT(JSON Web Token)包含三部分:
- Header:算法和token类型
- Payload:用户信息和声明
- Signature:验证签名
令牌增强示例:
public class CustomTokenEnhancer implements TokenEnhancer {
@Override
public OAuth2AccessToken enhance(OAuth2AccessToken accessToken,
OAuth2Authentication authentication) {
Map<String, Object> additionalInfo = new HashMap<>();
additionalInfo.put("organization", authentication.getName() + "ABC");
((DefaultOAuth2AccessToken) accessToken).setAdditionalInformation(additionalInfo);
return accessToken;
}
}实践建议:
- 使用非对称加密(RS256)替代HS256
- 设置合理的令牌过期时间(访问令牌1小时,刷新令牌30天)
- 实现令牌黑名单机制
2.3 单点登录(SSO)实现
基于Spring Security OAuth2实现SSO的架构:
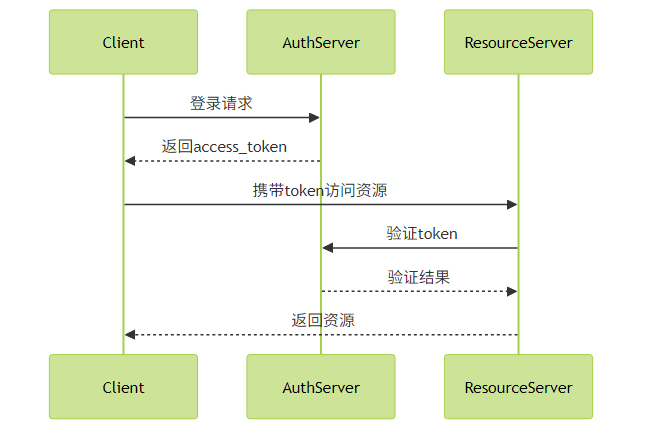
关键配置:
# 客户端配置
security:
oauth2:
client:
client-id: clientId
client-secret: secret
access-token-uri: http://auth-server/oauth/token
user-authorization-uri: http://auth-server/oauth/authorize
resource:
user-info-uri: http://auth-server/user/me实践建议:
- 使用专用授权服务器而非嵌入式
- 实现跨域支持(CORS配置)
- 结合前端框架(如Angular/React)实现完整的OAuth2流程
三、安全防护最佳实践
CSRF防护:对状态修改请求启用CSRF保护
http.csrf().csrfTokenRepository(CookieCsrfTokenRepository.withHttpOnlyFalse());HTTP安全头:自动添加安全头
http.headers() .contentSecurityPolicy("script-src 'self'") .and() .httpStrictTransportSecurity() .and() .xssProtection();会话管理:
http.sessionManagement() .maximumSessions(1) .expiredUrl("/login?expired");审计日志:记录关键安全事件
@Bean public AuditorAware<String> auditorAware() { return () -> Optional.ofNullable(SecurityContextHolder.getContext()) .map(SecurityContext::getAuthentication) .filter(Authentication::isAuthenticated) .map(Authentication::getName); }
结语
Spring Security提供了全面的企业级安全解决方案,结合OAuth2和JWT可以实现灵活的分布式安全架构。实际应用中应注意:
- 根据业务场景选择合适的认证授权方案
- 令牌管理要平衡安全性与用户体验
- 定期进行安全审计和漏洞扫描
- 保持依赖库的最新版本
通过合理配置和扩展,Spring Security能够满足从单体应用到微服务架构的各种安全需求。