Spring Cloud Stream消息驱动微服务架构指南
Spring Cloud Stream:构建高效消息驱动微服务架构
一、Spring Cloud Stream核心概念
Spring Cloud Stream是一个用于构建消息驱动微服务的框架,它通过统一的消息编程模型简化了不同消息中间件的集成。
1.1 绑定器(Binder)概念
绑定器是Spring Cloud Stream的核心抽象,负责与特定消息中间件(如RabbitMQ、Kafka)的集成。
@Configuration
public class BinderConfiguration {
@Bean
public Binder<MessageChannel> rabbitBinder(
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return new RabbitMessageChannelBinder(connectionFactory);
}
}实践建议:
- 生产环境中建议使用
spring-cloud-stream-binder-rabbit或spring-cloud-stream-binder-kafka官方绑定器 - 自定义绑定器时需实现
Binder接口
1.2 消息通道(Message Channel)
Spring Cloud Stream提供了两种预定义通道:
- 输入通道(
@Input):用于接收消息 - 输出通道(
@Output):用于发送消息
public interface OrderProcessor {
String ORDER_INPUT = "orderInput";
String ORDER_OUTPUT = "orderOutput";
@Input(ORDER_INPUT)
SubscribableChannel orderInput();
@Output(ORDER_OUTPUT)
MessageChannel orderOutput();
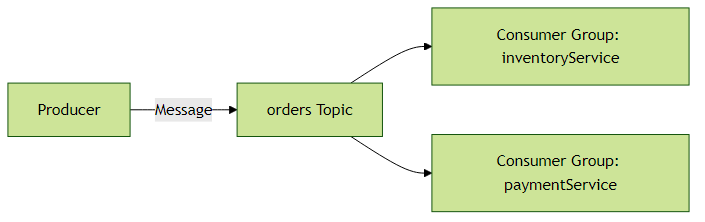
}1.3 消息分组(Consumer Groups)
消息分组确保同一组的消费者只有一个实例处理消息,实现负载均衡。
spring:
cloud:
stream:
bindings:
orderInput:
destination: orders
group: inventoryService拓扑关系图:
1.4 分区支持(Partitioning)
分区允许将相关消息路由到同一消费者实例,保证顺序处理。
spring:
cloud:
stream:
bindings:
orderOutput:
destination: orders
producer:
partition-key-expression: payload.orderId
partition-count: 3二、RabbitMQ深度集成
2.1 交换机与队列配置
@Bean
public Declarables declarables() {
return new Declarables(
new DirectExchange("orders.direct"),
new Queue("orders.queue"),
new Binding("orders.queue",
Binding.DestinationType.QUEUE,
"orders.direct",
"orders.routing",
null)
);
}2.2 消息确认机制
spring:
rabbitmq:
listener:
simple:
acknowledge-mode: manual # 手动确认@StreamListener(OrderProcessor.ORDER_INPUT)
public void handleOrder(Order order,
@Header(AmqpHeaders.CHANNEL) Channel channel,
@Header(AmqpHeaders.DELIVERY_TAG) long tag) {
try {
// 处理业务逻辑
channel.basicAck(tag, false);
} catch (Exception e) {
channel.basicNack(tag, false, true);
}
}实践建议:
- 生产环境建议使用手动确认模式
- 重试次数建议通过
spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.retry配置
三、Kafka高级集成
3.1 主题管理与消费者组
spring:
cloud:
stream:
kafka:
binder:
brokers: localhost:9092
auto-create-topics: true
bindings:
orderInput:
destination: orders
group: inventory-group
consumer:
auto-offset-reset: latest3.2 消息分区策略
@Bean
public ProducerFactory<String, Order> producerFactory() {
Map<String, Object> config = new HashMap<>();
config.put(ProducerConfig.PARTITIONER_CLASS_CONFIG,
OrderPartitioner.class);
// 其他配置...
return new DefaultKafkaProducerFactory<>(config);
}
public class OrderPartitioner implements Partitioner {
@Override
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes,
Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) {
return ((Order)value).getCustomerId().hashCode() %
cluster.partitionCountForTopic(topic);
}
}四、性能优化实践
批量处理(Kafka):
spring: cloud: stream: kafka: binder: producer: batch-size: 16384 buffer-memory: 33554432消费者并发:
spring: cloud: stream: bindings: orderInput: consumer: concurrency: 3消息压缩:
spring: cloud: stream: kafka: binder: producer: compression-type: snappy
五、常见问题解决方案
- 消息重复消费:
- 实现幂等处理
- 使用
@KafkaListener(idempotent = true) - 消息顺序保证:
- 使用分区键确保相关消息进入同一分区
- 单个分区单消费者模式
- 消息积压处理:
- 动态扩展消费者实例
- 使用死信队列处理失败消息
@Bean
public ListenerContainerCustomizer<AbstractMessageListenerContainer>
containerCustomizer() {
return (container, dest, group) -> {
if (container instanceof ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer) {
((ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer) container)
.setConcurrency(scaleOutFactor);
}
};
}结语
Spring Cloud Stream通过抽象的消息编程模型,显著简化了消息中间件的集成复杂度。在实际应用中,建议:
- 根据业务场景选择合适的消息中间件
- 合理设计消息分组和分区策略
- 实现完善的错误处理和监控机制
- 定期进行性能测试和调优
通过合理运用Spring Cloud Stream,可以构建出高可靠、高性能的消息驱动微服务架构。