Spring Cloud Stream消息驱动架构实战指南
Spring Cloud消息驱动:构建高效事件驱动架构
一、Spring Cloud Stream核心架构
Spring Cloud Stream是一个用于构建消息驱动微服务的框架,它通过抽象化的消息中间件访问层,让开发者能够专注于业务逻辑而不用关心底层消息系统的实现细节。
绑定器(Binder)与消息通道(Channel)
绑定器是Spring Cloud Stream的核心抽象,负责与特定消息中间件(如RabbitMQ、Kafka)的集成。每个绑定器对应一种消息中间件实现,通过简单的配置即可切换。
// 消息生产者示例
@SpringBootApplication
public class ProducerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ProducerApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public Supplier<String> messageProducer() {
return () -> "Hello " + new Date();
}
}
// 消息消费者示例
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConsumerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConsumerApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public Consumer<String> messageConsumer() {
return message -> System.out.println("Received: " + message);
}
}配置示例:
spring:
cloud:
stream:
bindings:
messageProducer-out-0: # 生产者通道
destination: notifications
content-type: text/plain
messageConsumer-in-0: # 消费者通道
destination: notifications
group: notification-service
content-type: text/plain实践建议:
- 为每个微服务定义清晰的通道命名规范(如
<service>.<action>) - 始终指定content-type以避免序列化问题
- 生产环境建议启用消息持久化
消费者组(Consumer Groups)
消费者组是确保消息只被消费一次的关键机制。同一组内的消费者共享消息负载,而不同组的消费者会各自收到完整消息副本。
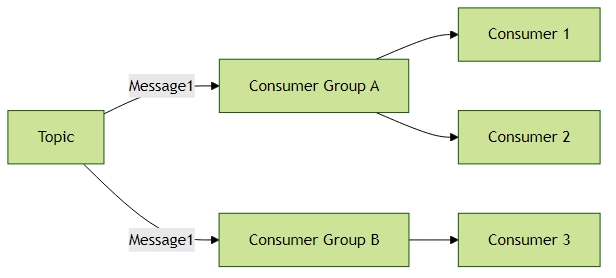
关键配置:
spring:
cloud:
stream:
bindings:
input:
destination: orders
group: inventory-service # 消费者组名称实践建议:
- 消费者组名称应与服务名称一致
- 合理设置并发消费者数量(
spring.cloud.stream.bindings.input.consumer.concurrency) - 监控消费者滞后情况(特别是Kafka)
消息分区(Partitioning)
消息分区允许将相关消息路由到同一消费者实例,确保有序处理或状态维护。
// 分区键提取器
@Bean
public PartitionKeyExtractor partitionKeyExtractor() {
return message -> {
Order order = (Order) message.getPayload();
return order.getCustomerId();
};
}分区配置:
spring:
cloud:
stream:
bindings:
output:
destination: orders
producer:
partition-key-expression: payload.customerId
partition-count: 5实践建议:
- 选择具有良好分布特性的分区键(避免热点)
- 分区数量应与消费者实例数保持比例关系
- 测试分区再平衡对业务的影响
二、Spring Cloud Bus:分布式系统的神经系统
Spring Cloud Bus通过轻量级消息代理连接分布式系统的节点,用于广播状态更改(如配置更新)或管理命令。
配置刷新广播
最典型的应用场景是当配置中心更新后,通过Bus通知所有服务刷新配置,而无需逐个重启。
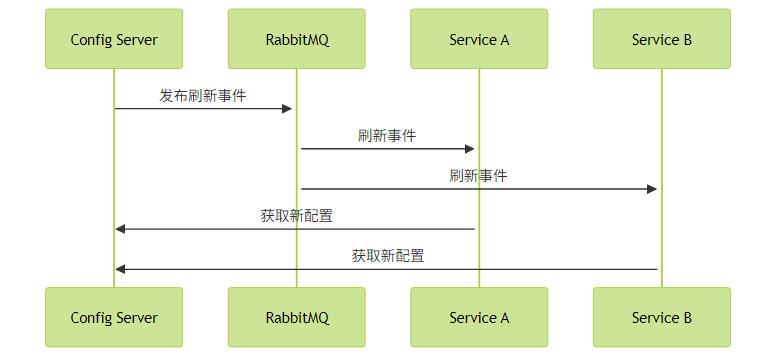
触发刷新:
# 向任意服务实例发送POST请求
curl -X POST http://service-instance:port/actuator/bus-refresh高级配置:
spring:
cloud:
bus:
enabled: true
trace:
enabled: true # 启用事件跟踪
id: ${spring.application.name}:${server.port} # 自定义实例ID实践建议:
- 生产环境应限制
/bus-refresh端点的访问权限 - 考虑使用Webhook自动触发刷新
- 监控配置刷新失败的情况
事件驱动架构(EDA)实现
Spring Cloud Bus可用于构建更复杂的事件驱动系统,实现服务间的松耦合通信。
自定义事件示例:
// 定义事件
public class InventoryChangedEvent {
private String productId;
private int newQuantity;
// getters/setters...
}
// 发布事件
@Autowired
private ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher;
public void updateInventory(InventoryUpdate update) {
// 更新库存...
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InventoryChangedEvent(
update.getProductId(),
getCurrentQuantity()
));
}
// 监听事件
@EventListener
public void handleInventoryChange(InventoryChangedEvent event) {
// 处理库存变更通知
}实践建议:
- 定义清晰的事件命名规范(
<聚合根><动作>Event) - 事件应携带足够的信息,避免接收方需要额外查询
- 考虑事件的版本兼容性
三、消息中间件选型与优化
RabbitMQ与Kafka比较
| 特性 | RabbitMQ | Kafka |
|---|---|---|
| 消息模型 | 队列/Exchange | 主题/分区 |
| 吞吐量 | 中等(万级/秒) | 高(十万级/秒) |
| 延迟 | 低(毫秒级) | 中(毫秒到秒) |
| 消息保证 | ACK/NACK | 精确一次语义 |
| 适用场景 | 业务解耦、延迟消息 | 日志处理、流式计算 |
性能优化技巧
批量处理(Kafka):
spring: cloud: stream: kafka: binder: producer: batch-size: 16384 # 16KB消费者并发:
spring: cloud: stream: bindings: input: consumer: concurrency: 3 # 每个实例的消费者线程数错误处理:
@Bean public Consumer<Message<String>> errorDemo() { return message -> { try { process(message); } catch (Exception e) { // 自定义错误处理 message.getHeaders().get(KafkaHeaders.ACKNOWLEDGMENT) .nack(Duration.ofSeconds(30)); // 延迟重试 } }; }
四、监控与问题排查
关键监控指标
生产者端:
- 消息发送成功率
- 发送延迟
- 队列积压(RabbitMQ)
消费者端:
- 消费延迟
- 处理耗时
- 错误率
诊断工具集成
// 启用消息追踪
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableBinding(Processor.class)
public class MyApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApp.class, args);
}
@Bean
public MessageChannelCustomizer channelCustomizer() {
return (channel, channelName) -> {
if (channel instanceof SubscribableChannel) {
((SubscribableChannel) channel).addInterceptor(new TracingChannelInterceptor());
}
};
}
}日志关联:
2023-03-15 14:30:00 [consumer-1] INFO c.e.MyConsumer - [traceId=abc123, spanId=def456] Received order: Order123
2023-03-15 14:30:01 [consumer-1] INFO c.e.MyService - [traceId=abc123, spanId=ghi789] Processing order...五、最佳实践总结
消息设计原则:
- 保持消息小巧(<1MB)
- 使用显式模式(如Protobuf)
- 包含消息版本信息
错误处理策略:
- 实现死信队列(DLQ)
- 设置合理的重试策略
- 记录完整的错误上下文
安全考虑:
spring: rabbitmq: ssl: enabled: true username: ${MQ_USER} password: ${MQ_PASS}测试策略:
@SpringBootTest @EmbeddedKafka(topics = {"testTopic"}) class KafkaStreamTest { @Autowired private EmbeddedKafkaBroker kafka; @Test void testMessageFlow() { // 发送测试消息并验证处理结果 } }
通过合理运用Spring Cloud Stream和Spring Cloud Bus,开发者可以构建出高弹性、松耦合的分布式系统,实现真正的云原生应用架构。