Nginx日志配置与监控分析实战指南
Nginx日志与监控分析实战指南
一、日志配置的艺术
1.1 自定义日志格式
Nginx默认的日志格式可能无法满足精细化分析需求,通过log_format指令可以自定义日志格式:
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] '
'"$request" $status $body_bytes_sent '
'"$http_referer" "$http_user_agent" '
'rt=$request_time uct="$upstream_connect_time" '
'uht="$upstream_header_time" urt="$upstream_response_time"';
log_format api_log '[$time_iso8601] client=$remote_addr '
'method=$request_method uri=$request_uri '
'status=$status req_time=$request_time '
'upstream_time=$upstream_response_time '
'user_agent="$http_user_agent"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
access_log /var/log/nginx/api.access.log api_log;
}实践建议:
- 生产环境建议包含
$request_time和$upstream_response_time用于性能分析 - 对API服务单独配置日志格式,便于后续解析处理
- 使用
$time_iso8601替代$time_local获得标准时间格式
1.2 条件日志记录
通过map指令实现按条件记录日志,减少无效日志存储:
map $status $loggable {
~^[23] 0; # 2xx/3xx状态码不记录
default 1; # 其他状态码记录
}
map $request_uri $skip_healthcheck {
/healthcheck 1;
default 0;
}
server {
access_log /var/log/nginx/error.access.log combined if=$loggable;
access_log /var/log/nginx/full.access.log combined if=$skip_healthcheck;
}实践建议:
- 对健康检查路径单独处理,避免日志爆炸
- 404错误建议单独记录,便于分析非法扫描行为
- 结合
map和if实现复杂的日志过滤逻辑
二、监控集成方案
2.1 Stub Status模块
内置的Stub Status模块提供基础监控指标:
server {
listen 127.0.0.1:8080;
location /nginx_status {
stub_status on;
access_log off;
allow 127.0.0.1;
deny all;
}
}输出示例:
Active connections: 291
server accepts handled requests
16630948 16630948 31070465
Reading: 6 Writing: 179 Waiting: 106 指标说明:
- Active connections: 当前活跃连接数
- Reading: 正在读取请求头的连接数
- Writing: 正在处理请求或发送响应的连接数
- Waiting: 空闲keep-alive连接数
2.2 Prometheus + Grafana方案
使用nginx-prometheus-exporter采集指标:
# docker-compose.yml示例
services:
nginx-exporter:
image: nginx/nginx-prometheus-exporter
ports:
- "9113:9113"
command:
- '-nginx.scrape-uri=http://nginx:8080/nginx_status'Grafana仪表板关键指标:
- 请求率/QPS
- 连接状态分布
- 4xx/5xx错误率
- 请求处理时间百分位
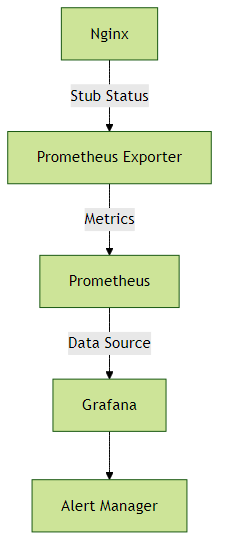
实践建议:
- 设置请求处理时间P99告警阈值
- 监控Waiting连接数异常增长
- 对upstream响应时间单独监控
2.3 ELK错误日志分析
典型ELK栈配置:
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;
# Logstash配置示例
input {
file {
path => "/var/log/nginx/error.log"
type => "nginx-error"
}
}
filter {
grok {
match => { "message" => "%{TIMESTAMP_ISO8601:timestamp} \[%{LOGLEVEL:severity}\] %{POSINT:pid}#%{NUMBER}: %{GREEDYDATA:errormessage}" }
}
}Kibana分析场景:
- 错误级别分布饼图
- 高频错误关键词词云
- 错误发生时间趋势
实践建议:
- 对
warn级别以上日志单独监控 - 使用
grok提取连接ID便于追踪 - 建立常见错误的知识库文档
三、高级技巧
3.1 日志轮转优化
使用logrotate避免日志文件过大:
/var/log/nginx/*.log {
daily
missingok
rotate 14
compress
delaycompress
notifempty
create 0640 www-data adm
sharedscripts
postrotate
[ ! -f /var/run/nginx.pid ] || kill -USR1 `cat /var/run/nginx.pid`
endscript
}3.2 实时日志分析
使用GoAccess实现实时分析:
goaccess /var/log/nginx/access.log --log-format=COMBINED --real-time-html --port=78903.3 结构化日志实践
JSON格式日志便于解析:
log_format json_combined escape=json
'{'
'"time_local":"$time_local",'
'"remote_addr":"$remote_addr",'
'"request":"$request",'
'"status": "$status",'
'"body_bytes_sent":"$body_bytes_sent",'
'"request_time":"$request_time",'
'"http_referrer":"$http_referer",'
'"http_user_agent":"$http_user_agent"'
'}';四、总结
日志配置黄金法则:
- 业务日志与访问日志分离
- 关键性能指标必须记录
- 生产环境禁用debug级别日志
监控告警最佳实践:
- 核心指标:错误率、延迟、流量
- 设置分级告警阈值
- 保留至少30天的监控数据
- 排错流程建议:

通过合理的日志配置和监控体系,可以快速定位性能瓶颈和安全问题,为系统稳定性提供有力保障。