Java性能监控与JVM调优实战:内存测量与集合基准测试
Java性能监控与调优实战:JVM指标与集合基准测试
一、JVM内存指标深度解析
1.1 对象内存占用测量
在性能调优中,准确测量对象内存占用是基础工作。Java提供了Instrumentation接口来实现这一功能:
import java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation;
public class ObjectSizeCalculator {
private static Instrumentation instrumentation;
public static void premain(String args, Instrumentation inst) {
instrumentation = inst;
}
public static long getObjectSize(Object o) {
if (instrumentation == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Instrumentation not initialized");
}
return instrumentation.getObjectSize(o);
}
}使用示例测量不同集合的内存占用:
List<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(100);
List<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
Map<Integer, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>(100);
System.out.println("ArrayList(空): " + ObjectSizeCalculator.getObjectSize(arrayList));
System.out.println("LinkedList(空): " + ObjectSizeCalculator.getObjectSize(linkedList));
System.out.println("HashMap(空): " + ObjectSizeCalculator.getObjectSize(hashMap));实践建议:
- 对于小数据集(1000元素以下),ArrayList通常比LinkedList占用更少内存
- HashMap的初始容量设置应基于预期元素数量,避免频繁扩容
- 使用
-javaagent参数加载Instrumentation代理
1.2 GC对数据结构的影响
不同数据结构对GC压力有显著差异:
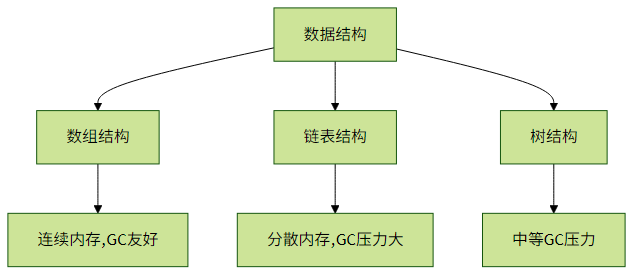
GC友好设计原则:
- 优先使用数组支持的集合(ArrayList而非LinkedList)
- 避免创建大量小对象(如使用原始类型集合库)
- 对于长期存活的大集合,考虑使用
java.nio.ByteBuffer堆外内存
二、JMH基准测试实战
2.1 JMH测试环境搭建
添加Maven依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.openjdk.jmh</groupId>
<artifactId>jmh-core</artifactId>
<version>1.35</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.openjdk.jmh</groupId>
<artifactId>jmh-generator-annprocess</artifactId>
<version>1.35</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>2.2 集合操作性能测试案例
测试ArrayList与LinkedList的访问性能:
@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)
@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)
@State(Scope.Thread)
public class ListBenchmark {
@Param({"1000", "10000", "100000"})
private int size;
private List<Integer> arrayList;
private List<Integer> linkedList;
private Random random;
@Setup
public void setup() {
arrayList = new ArrayList<>(size);
linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int value = random.nextInt();
arrayList.add(value);
linkedList.add(value);
}
}
@Benchmark
public Integer arrayListGet() {
return arrayList.get(size / 2);
}
@Benchmark
public Integer linkedListGet() {
return linkedList.get(size / 2);
}
}典型测试结果分析:
| 操作 | 集合类型 | 10,000元素耗时(ns) | 相对性能 |
|---|---|---|---|
| get() | ArrayList | 5.2 | 基准 |
| get() | LinkedList | 12500.7 | 慢2400倍 |
2.3 高级测试技巧
测试GC影响:
@Benchmark @Warmup(iterations = 3, time = 1) @Measurement(iterations = 5, time = 1) @Fork(2) public void testWithGC(Blackhole bh) { List<Integer> tempList = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { tempList.add(i); } bh.consume(tempList); // 防止被优化掉 }多线程测试:
@Benchmark @Threads(4) public void concurrentAccess() { // 测试并发访问性能 }
实践建议:
- 始终在测试中包含预热阶段(避免JIT编译影响)
- 对于并发集合,测试不同线程数下的性能
- 使用
@Param测试不同数据规模 - 关注性能的百分位数(使用
@OutputTimeUnit和@BenchmarkMode(Mode.SampleTime))
三、性能调优黄金法则
- 测量优先法则:永远基于实际测量数据做优化决策
- 数据结构选择矩阵:
| 场景 | 推荐结构 | 替代方案 |
|---|---|---|
| 随机访问多 | ArrayList | ArrayDeque |
| 频繁插入删除 | LinkedList | TreeSet |
| 键值查询 | HashMap | ConcurrentHashMap |
| 范围查询 | TreeMap | SkipList |
内存优化检查表:
- [ ] 是否设置了合理的初始容量?
- [ ] 是否使用了原始类型特化集合(如FastUtil)?
- [ ] 大集合是否考虑分片或堆外存储?
- [ ] 是否避免了不必要的对象包装?
四、生产环境监控集成
将JVM指标与APM工具(如Prometheus)集成:
// 使用Micrometer暴露JVM指标
public class JvmMetricsConfig {
@Bean
MeterRegistryCustomizer<MeterRegistry> metricsCommonTags() {
return registry -> {
registry.config().commonTags("application", "performance-demo");
new JvmMemoryMetrics().bindTo(registry);
new JvmGcMetrics().bindTo(registry);
new JvmThreadMetrics().bindTo(registry);
};
}
}关键监控指标:
jvm_memory_used_bytes内存使用量jvm_gc_pause_secondsGC停顿时间jvm_classes_loaded类加载数量
通过结合JVM指标监控和精准的基准测试,开发者可以建立起完整的性能优化闭环,从发现问题到验证解决方案都能做到数据驱动。