Java并发通信:同步与异步模式实践指南
Java并发通信模式:同步与异步的实践指南
并发通信是Java多线程编程的核心问题之一,本文将深入探讨Java中同步和异步通信的主要模式及其实现方式。
一、同步通信模式
同步通信要求发送方和接收方必须同时准备好才能进行数据交换,具有强一致性的特点。
1. 共享内存模型
共享内存是最常见的线程通信方式,通过读写内存中的公共状态进行信息交换。
volatile关键字
public class VolatileExample {
private volatile boolean flag = false;
public void writer() {
flag = true; // 写操作
}
public void reader() {
while (!flag) { // 读操作
// 等待flag变为true
}
System.out.println("Flag is now true");
}
}实践建议:
- 仅当变量真正独立于程序其他状态时使用volatile
- 适合一写多读的场景,不保证复合操作的原子性
Atomic原子类
public class AtomicExample {
private AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(0);
public void increment() {
counter.incrementAndGet();
}
public int get() {
return counter.get();
}
}实践建议:
- 比synchronized性能更好,适合简单原子操作
- 复杂操作仍需使用锁机制
2. 管道通信
public class PipeExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
final PipedOutputStream output = new PipedOutputStream();
final PipedInputStream input = new PipedInputStream(output);
Thread writer = new Thread(() -> {
try {
output.write("Hello from pipe!".getBytes());
output.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
Thread reader = new Thread(() -> {
try {
int data;
while ((data = input.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) data);
}
input.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
writer.start();
reader.start();
}
}实践建议:
- 适合线程间顺序数据传输
- 实际开发中较少使用,通常用BlockingQueue替代
二、异步通信模式
异步通信允许发送方和接收方在不同时间点进行交互,提高了系统的响应性和吞吐量。
1. 消息队列(BlockingQueue)
public class BlockingQueueExample {
private final BlockingQueue<String> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(10);
public void produce() throws InterruptedException {
queue.put("Message " + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
public String consume() throws InterruptedException {
return queue.take();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueueExample example = new BlockingQueueExample();
// 生产者线程
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
example.produce();
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}).start();
// 消费者线程
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
String message = example.consume();
System.out.println("Received: " + message);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}).start();
}
}实践建议:
根据场景选择合适的队列实现:
ArrayBlockingQueue:固定大小,公平性可选LinkedBlockingQueue:可选边界,吞吐量更高PriorityBlockingQueue:优先级排序SynchronousQueue:直接传递,无缓冲
- 考虑使用
put/take(阻塞)或offer/poll(非阻塞)方法
2. 事件总线(EventBus)
Guava的EventBus提供了一种发布-订阅模式的实现:
public class EventBusExample {
public static class MessageEvent {
private final String message;
public MessageEvent(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
}
public static class EventListener {
@Subscribe
public void onMessage(MessageEvent event) {
System.out.println("Received: " + event.getMessage());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventBus eventBus = new EventBus();
eventBus.register(new EventListener());
// 发布事件
eventBus.post(new MessageEvent("Hello EventBus!"));
}
}实践建议:
- 适合组件间松耦合通信
- 注意事件处理方法的线程安全
- 考虑使用
AsyncEventBus实现异步处理
三、模式选择指南
同步 vs 异步选择矩阵
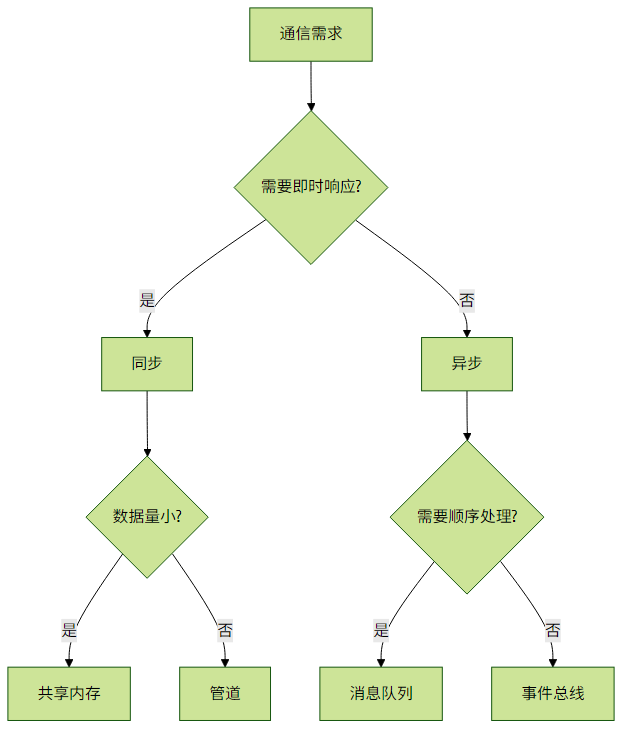
实践建议:
- 对于状态更新,优先考虑volatile和Atomic类
- 对于生产者-消费者模式,使用BlockingQueue
- 对于组件间解耦,考虑EventBus
- 避免过度使用管道,它在Java中性能较差
四、常见问题与解决方案
消息丢失问题:
- 使用持久化队列(如Kafka)
- 实现确认机制
内存泄漏风险:
- 监控队列大小
- 设置合理的队列容量
线程饥饿:
- 使用公平锁
- 限制最大处理时间
调试困难:
- 为消息添加唯一ID
- 实现日志追踪
通过合理选择并发通信模式,可以构建出高效、可维护的多线程Java应用程序。在实际开发中,通常需要组合使用多种模式来满足复杂的需求。