Spring Security配置与JWT集成实战指南
Spring Security 常规用法详解
Spring Security 是 Spring 生态中功能强大的安全框架,本文将深入讲解其常规用法,包括基础配置、用户认证、权限控制和 JWT 集成等核心功能。
一、基础配置
1. 最小化安全配置
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/public/**").permitAll() // 公共资源放行
.anyRequest().authenticated() // 其他请求需认证
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login").permitAll() // 自定义登录页
.and()
.logout().permitAll(); // 允许注销
}
}关键点解析:
@EnableWebSecurity启用安全配置authorizeRequests()定义URL访问规则formLogin()启用表单登录,可自定义登录页路径logout()配置注销功能
实践建议:
- 生产环境建议禁用默认的HTTP Basic认证(
.httpBasic().disable()) - 静态资源(CSS/JS等)应放在
/public/或/static/目录下
二、自定义用户认证
1. 基于数据库的用户认证
@Bean
public UserDetailsService userDetailsService(UserRepository userRepository) {
return username -> {
User user = userRepository.findByUsername(username)
.orElseThrow(() -> new UsernameNotFoundException("用户不存在"));
return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(
user.getUsername(),
user.getPassword(),
user.isEnabled(), true, true, true,
AuthorityUtils.createAuthorityList(user.getRoles())
);
};
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); // 推荐使用BCrypt加密
}认证流程:
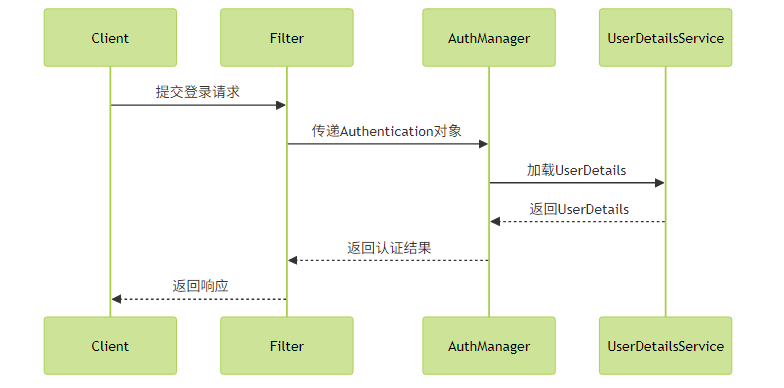
实践建议:
- 密码必须使用
PasswordEncoder加密存储 - 实现
UserDetails接口比直接使用框架提供的User类更灵活 - 用户状态(启用/禁用)应纳入认证逻辑
三、方法级权限控制
1. 启用方法安全
@Configuration
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(
prePostEnabled = true, // 启用@PreAuthorize等注解
securedEnabled = true // 启用@Secured注解
)
public class MethodSecurityConfig {
}2. 权限注解使用示例
@Service
public class AdminService {
// 基于角色控制
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
public void deleteUser(Long userId) { ... }
// 基于权限控制
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('USER_DELETE')")
public void deleteUser(Long userId) { ... }
// 基于业务参数控制
@PreAuthorize("#userId == authentication.principal.id")
public void viewProfile(Long userId) { ... }
// 方法调用后权限检查
@PostAuthorize("returnObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Document getDocument(Long docId) { ... }
}实践建议:
@PreAuthorize比@Secured更灵活,支持SpEL表达式- 复杂权限逻辑可自定义
PermissionEvaluator - 服务层方法应始终进行权限检查,不能仅依赖Web层保护
四、JWT集成
1. JWT过滤器配置
public class JwtAuthenticationFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
String token = resolveToken(request);
if (token != null && validateToken(token)) {
Authentication auth = getAuthentication(token);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(auth);
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
private String resolveToken(HttpServletRequest request) {
String bearerToken = request.getHeader("Authorization");
if (StringUtils.hasText(bearerToken) && bearerToken.startsWith("Bearer ")) {
return bearerToken.substring(7);
}
return null;
}
}2. 安全配置适配
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.csrf().disable() // JWT通常禁用CSRF
.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS) // 无状态会话
.and()
.addFilterBefore(jwtAuthenticationFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class)
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/api/auth/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated();
}
@Bean
public JwtAuthenticationFilter jwtAuthenticationFilter() {
return new JwtAuthenticationFilter();
}JWT处理流程:
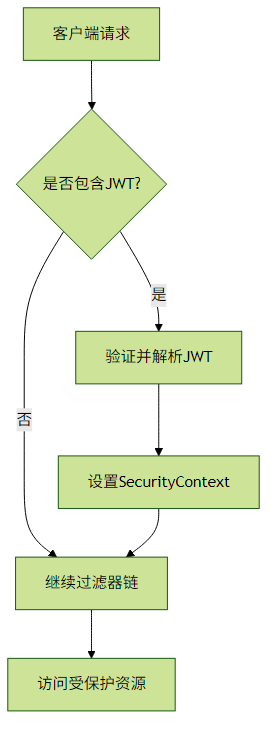
实践建议:
- JWT应设置合理的过期时间(通常2小时)
- 实现令牌刷新机制,避免频繁登录
- 敏感操作应要求重新认证(如修改密码)
五、最佳实践总结
- 分层防护:Web层+方法层双重保护
- 最小权限:遵循最小权限原则分配角色
- 日志审计:记录关键安全事件(登录失败、权限变更等)
- 定期审查:检查安全配置和依赖库漏洞
测试覆盖:
@Test @WithMockUser(roles = "ADMIN") public void testAdminAccess() { mockMvc.perform(get("/admin")) .andExpect(status().isOk()); }
通过合理配置这些常规功能,可以构建既安全又易维护的应用程序安全体系。
评论已关闭