Shiro性能优化与安全加固实战指南之一
Shiro常见问题与优化实战指南
Shiro作为轻量级安全框架,在实际应用中常会遇到性能、安全和调试方面的问题。本文将针对这些痛点提供系统性解决方案。
一、性能优化策略
1. 缓存策略优化
Shiro的认证授权信息默认不缓存,频繁查询Realm会导致性能瓶颈。推荐采用多级缓存方案:
// 配置EhCache缓存示例
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager() {
EhCacheManager cacheManager = new EhCacheManager();
cacheManager.setCacheManagerConfigFile("classpath:ehcache.xml");
return cacheManager;
}
// ehcache.xml配置片段
<cache name="shiroAuthorizationCache"
maxEntriesLocalHeap="10000"
timeToLiveSeconds="3600"
timeToIdleSeconds="1800"/>实践建议:
- 权限缓存TTL建议设置30-60分钟(敏感系统可缩短)
- 用户认证缓存TTL可适当延长(如2小时)
- 生产环境推荐使用Redis分布式缓存
2. 减少Realm重复查询
通过重写doGetAuthorizationInfo方法实现按需加载:
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
if (principals == null) {
return null;
}
// 从缓存获取已有权限
AuthorizationInfo info = getAuthorizationCache().get(principals);
if (info != null) {
return info;
}
// 缓存不存在时查询数据库
User user = userService.findByUsername(principals.getPrimaryPrincipal());
SimpleAuthorizationInfo authorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
authorizationInfo.setRoles(user.getRoles());
authorizationInfo.setStringPermissions(user.getPermissions());
// 存入缓存
getAuthorizationCache().put(principals, authorizationInfo);
return authorizationInfo;
}二、安全加固方案
1. 防暴力破解实现
自定义CredentialsMatcher实现登录限制:
public class RetryLimitCredentialsMatcher extends HashedCredentialsMatcher {
private Cache<String, AtomicInteger> passwordRetryCache;
public RetryLimitCredentialsMatcher(CacheManager cacheManager) {
passwordRetryCache = cacheManager.getCache("passwordRetryCache");
}
@Override
public boolean doCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) {
String username = (String) token.getPrincipal();
AtomicInteger retryCount = passwordRetryCache.get(username);
if (retryCount == null) {
retryCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
passwordRetryCache.put(username, retryCount);
}
if (retryCount.incrementAndGet() > 5) {
throw new ExcessiveAttemptsException("密码错误次数超过限制");
}
boolean matches = super.doCredentialsMatch(token, info);
if (matches) {
passwordRetryCache.remove(username);
}
return matches;
}
}2. 敏感操作二次验证
通过自定义Filter实现关键操作验证:
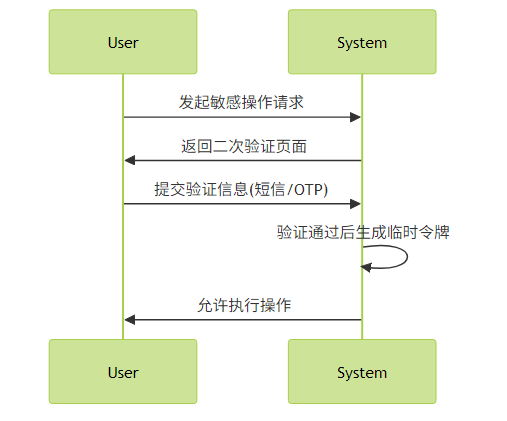
实现代码片段:
@RequiresPermissions("account:transfer")
@RequestMapping("/transfer")
public String transfer(@RequestParam double amount,
@RequestParam String code) {
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// 检查二次验证
if (!subject.hasRole("temp_token")) {
return "redirect:/verify?operation=transfer";
}
// 执行业务逻辑
accountService.transfer(amount);
return "success";
}三、调试技巧
1. 日志配置
在logback.xml中增加Shiro调试日志:
<logger name="org.apache.shiro" level="DEBUG"/>
<logger name="org.apache.shiro.web.filter" level="TRACE"/>典型日志分析:
DEBUG org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.ModularRealmAuthenticator - Authentication attempt for token [UsernamePasswordToken]
TRACE org.apache.shiro.subject.support.DelegatingSubject - Storing principals [admin]
DEBUG org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm - Get authorization info for admin2. 上下文获取技巧
// 获取当前用户最佳实践
public class SecurityUtils {
public static UserProfile getCurrentUser() {
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
if (subject.isAuthenticated()) {
return (UserProfile) subject.getPrincipal();
}
throw new UnauthenticatedException("用户未登录");
}
public static void checkPermission(String perm) {
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
subject.checkPermission(perm);
}
}常见问题排查清单:
- 权限不生效 → 检查缓存是否未及时清除
- 登录失败无提示 → 检查CredentialsMatcher实现
- Session丢失 → 检查分布式Session配置
- 注解无效 → 确保AOP代理生效
通过以上优化方案,可使Shiro在保证安全性的同时获得更好的性能表现。建议定期审计权限配置和缓存策略,特别是在用户权限频繁变更的场景下。
评论已关闭