Netty核心功能解析:网络通信与高性能设计之一
Netty核心功能深度解析:从网络通信到高性能设计
一、网络通信能力解析
1.1 TCP/UDP协议支持
Netty提供了完整的传输协议支持,通过不同的Channel实现类来区分协议类型:
// TCP服务端示例
ServerBootstrap tcpBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap()
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) // TCP协议
.handler(...);
// UDP服务端示例
Bootstrap udpBootstrap = new Bootstrap()
.channel(NioDatagramChannel.class) // UDP协议
.handler(...);协议选择建议:
- 需要可靠传输时选择TCP(如文件传输、金融交易)
- 对延迟敏感且可容忍丢包时选择UDP(如视频会议、实时游戏)
1.2 HTTP/WebSocket协议栈
Netty内置了完整的HTTP协议支持:
// HTTP服务端初始化
public class HttpServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
p.addLast(new HttpServerCodec()); // HTTP编解码
p.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(65536)); // 消息聚合
p.addLast(new HttpRequestHandler()); // 业务处理器
}
}WebSocket升级示例:
p.addLast(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/ws"));
p.addLast(new BinaryWebSocketFrameHandler());1.3 自定义协议开发
典型自定义协议开发模式:
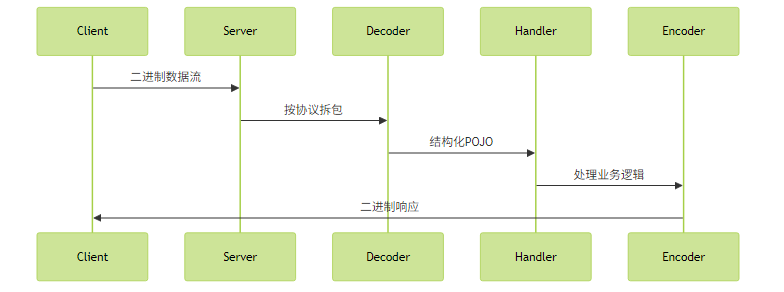
编解码器实现要点:
public class MyProtocolDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) {
if (in.readableBytes() < HEADER_SIZE) {
return; // 等待数据完整
}
in.markReaderIndex();
int length = in.readInt();
if (in.readableBytes() < length) {
in.resetReaderIndex(); // 重置读取位置
return;
}
byte[] content = new byte[length];
in.readBytes(content);
out.add(new MyProtocol(content));
}
}二、高性能设计原理
2.1 零拷贝技术
Netty通过ByteBuf实现了多种零拷贝优化:
Direct Buffer:
ByteBuf directBuf = Unpooled.directBuffer(1024); // 堆外内存复合缓冲区:
CompositeByteBuf compBuf = Unpooled.compositeBuffer(); compBuf.addComponents(true, headerBuf, bodyBuf);文件传输:
FileRegion region = new DefaultFileRegion(file, 0, file.length()); ctx.writeAndFlush(region);
内存使用建议:
- 频繁分配释放的小对象使用池化内存
- 生命周期长的缓冲区使用非池化内存
- 大文件传输务必使用FileRegion
2.2 内存池化技术
Netty内存池配置示例:
// 服务端内存池配置
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT);内存池工作流程:
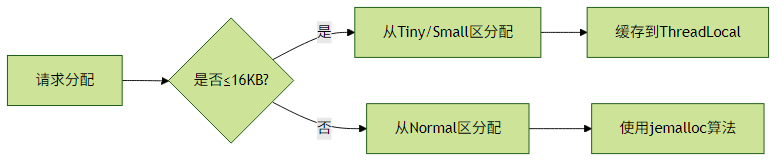
2.3 快速失败机制
流量控制实现示例:
public class WriteBufferWaterMarkHandler extends ChannelDuplexHandler {
@Override
public void channelWritabilityChanged(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
if (!ctx.channel().isWritable()) {
// 触发背压机制
log.warn("Channel {} not writable", ctx.channel());
}
}
}配置建议:
// 设置高低水位线
b.option(ChannelOption.WRITE_BUFFER_WATER_MARK,
new WriteBufferWaterMark(32 * 1024, 64 * 1024));三、核心功能实现
3.1 心跳检测机制
完整的心跳检测配置:
pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(30, 0, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
pipeline.addLast(new HeartbeatHandler());
// 自定义处理器示例
public class HeartbeatHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) {
if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) {
ctx.writeAndFlush(new PingMessage())
.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
}
}
}3.2 流量整形
全局流量控制实现:
// 全局限制为1MB/s
GlobalTrafficShapingHandler trafficHandler =
new GlobalTrafficShapingHandler(group, 1024 * 1024, 1024 * 1024);
// 单个Channel限速
ChannelTrafficShapingHandler perChannelHandler =
new ChannelTrafficShapingHandler(512 * 1024, 512 * 1024);流量整形建议:
- 生产环境建议使用动态限速策略
- 结合QoS策略实现差异化服务
- 注意监控writeLimit和readLimit的实际效果
3.3 SSL/TLS安全传输
双向认证配置示例:
SslContext sslCtx = SslContextBuilder.forServer(cert, key)
.trustManager(trustCert)
.clientAuth(ClientAuth.REQUIRE) // 强制客户端认证
.protocols("TLSv1.3") // 指定协议版本
.build();
pipeline.addFirst("ssl", sslCtx.newHandler(ch.alloc()));安全建议:
- 定期更新证书和私钥
- 禁用不安全的协议版本(如SSLv3)
- 使用强加密套件(如TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384)
四、扩展性设计
4.1 处理器链动态编排
动态修改Pipeline示例:
public class DynamicHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
if (msg instanceof LoginMessage) {
// 认证通过后添加业务处理器
ctx.pipeline().addAfter("auth", "business", new BusinessHandler());
}
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
}Pipeline设计原则:
- 处理器尽量保持无状态
- 耗时操作放在单独的线程池
- 注意处理器的执行顺序
4.2 多协议序列化支持
Protobuf集成示例:
// 解码器配置
pipeline.addLast(new ProtobufVarint32FrameDecoder());
pipeline.addLast(new ProtobufDecoder(MyMessage.getDefaultInstance()));
// 编码器配置
pipeline.addLast(new ProtobufVarint32LengthFieldPrepender());
pipeline.addLast(new ProtobufEncoder());序列化选型建议:
| 序列化方式 | 适用场景 | 性能对比 |
|---|---|---|
| Protobuf | 跨语言、高版本兼容 | ★★★★★ |
| JSON | 可读性要求高 | ★★★ |
| MessagePack | 二进制JSON | ★★★★ |
| Kryo | Java专有高性能 | ★★★★★ |
最佳实践总结
性能调优检查清单:
- 确认使用池化分配器(
PooledByteBufAllocator) - 检查是否合理使用Direct Buffer
- 验证线程模型配置是否匹配CPU核心数
- 监控内存泄漏(启用
ResourceLeakDetector)
- 确认使用池化分配器(
异常处理规范:
public class ExceptionHandler extends ChannelDuplexHandler { @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) { if (cause instanceof IOException) { // 网络异常处理 } else if (cause instanceof DecoderException) { // 编解码异常处理 } ctx.close(); } }生产环境建议配置:
// 工作线程组 EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup( Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2, new DefaultThreadFactory("netty-worker")); // 连接参数 bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024) .option(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, true) .childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true);
通过本文的深度解析,开发者可以全面掌握Netty的核心功能实现原理,并能在实际项目中合理应用各种高性能设计模式。建议结合具体业务场景进行针对性优化,持续监控关键性能指标,才能充分发挥Netty的高并发优势。
评论已关闭