Netty开发实践:服务端与客户端开发详解
Netty常规用法详解:服务端与客户端开发实践
Netty作为高性能网络框架,其常规用法是开发者必须掌握的核心技能。本文将深入讲解Netty在服务端和客户端开发中的标准模式,以及编解码器、粘包处理等关键技术的实现方式。
一、服务端开发全流程
1. 标准启动流程
Netty服务端的启动遵循固定模式,下面是典型代码实现:
// 1. 创建线程组
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); // 接收连接
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); // 处理业务
try {
// 2. 配置服务端
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128) // 连接队列大小
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true) // 保持长连接
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new MyServerHandler());
}
});
// 3. 绑定端口
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(8080).sync();
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// 4. 优雅关闭
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}关键组件说明:
bossGroup:处理连接请求的线程组,通常只需1个线程workerGroup:处理I/O操作的线程组,默认线程数为CPU核心数×2ServerBootstrap:服务端启动配置类
2. 业务处理实现
业务逻辑通过继承ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter实现:
public class MyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
try {
String request = buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
// 业务处理逻辑
String response = "Server response: " + request;
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(response, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
} finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}实践建议:
- 务必处理
exceptionCaught避免异常传播导致连接中断 - 使用
ReferenceCountUtil.release()释放ByteBuf资源 - 耗时操作应提交到业务线程池,避免阻塞EventLoop
二、客户端开发模式
1. 标准连接流程
客户端启动与服务端类似但更简单:
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true) // 禁用Nagle算法
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast(new StringEncoder())
.addLast(new StringDecoder())
.addLast(new MyClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture f = b.connect("127.0.0.1", 8080).sync();
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}2. 客户端处理器示例
public class MyClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) {
System.out.println("Server response: " + msg);
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ctx.writeAndFlush("Hello Server!");
}
}连接状态处理:
channelActive:连接建立时触发channelInactive:连接断开时触发channelRead0:收到消息时触发(自动释放消息资源)
三、编解码器实践
1. 内置编解码器使用
// 服务端Pipeline配置
pipeline.addLast(new StringDecoder()); // 字节→字符串
pipeline.addLast(new StringEncoder()); // 字符串→字节
pipeline.addLast(new ObjectEncoder()); // 对象→字节
pipeline.addLast(new ObjectDecoder(new ClassResolver() {
// 自定义类加载逻辑
}));2. 自定义协议实现
解码器示例:
public class MyDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) {
if (in.readableBytes() < 4) return; // 头部长度不足
in.markReaderIndex(); // 标记读取位置
int length = in.readInt();
if (in.readableBytes() < length) {
in.resetReaderIndex(); // 重置读取位置
return;
}
byte[] content = new byte[length];
in.readBytes(content);
out.add(new String(content));
}
}编码器示例:
public class MyEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<String> {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg, ByteBuf out) {
byte[] bytes = msg.getBytes();
out.writeInt(bytes.length); // 写入长度头
out.writeBytes(bytes); // 写入内容
}
}四、粘包/拆包解决方案
1. 常见处理方案对比
| 方案 | 实现类 | 适用场景 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 固定长度 | FixedLengthFrameDecoder | 定长协议 | 简单但浪费带宽 |
| 分隔符 | DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder | 文本协议 | 需处理转义字符 |
| 长度字段 | LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder | 二进制协议 | 最灵活的方案 |
2. 最佳实践:LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder
// 配置参数说明:
// maxFrameLength: 最大帧长度
// lengthFieldOffset: 长度字段偏移量
// lengthFieldLength: 长度字段字节数
// lengthAdjustment: 长度调整值
// initialBytesToStrip: 需要跳过的字节数
pipeline.addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(
1024, 0, 4, 0, 4));
pipeline.addLast(new MyDecoder());处理流程示意图:
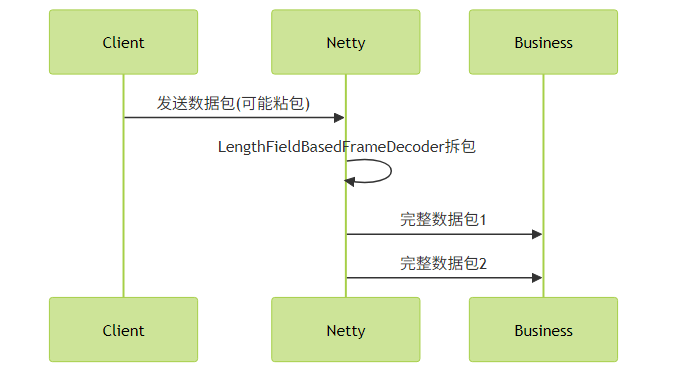
五、性能优化建议
线程组配置
- BossGroup通常1个线程足够
WorkerGroup默认CPU核心数×2
new NioEventLoopGroup(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2)
内存分配优化
// 使用池化直接内存 bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT);连接参数调优
.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 32 * 1024) // 接收缓冲区 .option(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, 32 * 1024) // 发送缓冲区 .option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 5000) // 连接超时
六、常见问题排查
内存泄漏检测
// 启动参数添加内存泄漏检测级别 -Dio.netty.leakDetection.level=PARANOID线程阻塞检查
// 添加阻塞检测处理器 pipeline.addLast(new BlockingDetectorHandler());连接状态监控
// 添加空闲检测 pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(60, 0, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
通过掌握这些常规用法,开发者可以构建出高性能、稳定的Netty网络应用。建议在实际项目中根据具体需求选择合适的配置方案,并通过性能测试验证效果。
评论已关闭