Netty高级特性:异步编程与性能调优指南
Netty高级特性:异步编程、性能调优与故障排查
1. 异步编程深度实践
1.1 ChannelFuture的异步回调
在Netty中,几乎所有I/O操作都是异步的。ChannelFuture提供了操作完成时的回调机制,这是Netty异步编程的核心。
典型用法:
ChannelFuture future = channel.writeAndFlush(message);
future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
System.out.println("Write successful");
} else {
System.err.println("Write error");
future.cause().printStackTrace();
}
}
});Java 8+简化写法:
channel.writeAndFlush(message).addListener(future -> {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
// 操作成功处理
} else {
// 操作失败处理
}
});实践建议:
- 对于关键操作(如连接建立、重要消息发送)必须添加监听器
- 避免在回调中执行阻塞操作,这会阻塞EventLoop线程
- 使用
isSuccess()检查操作结果,而非isDone()
1.2 Promise与Future的扩展使用
Promise是Netty对Future的扩展,允许主动设置操作结果。
创建自定义异步任务:
EventLoop eventLoop = channel.eventLoop();
Promise<String> promise = eventLoop.newPromise();
// 在其他线程完成Promise
executorService.execute(() -> {
try {
String result = doLongRunningTask();
promise.setSuccess(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
promise.setFailure(e);
}
});
// 添加监听器
promise.addListener(future -> {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
System.out.println("Result: " + future.get());
}
});组合多个异步操作:
ChannelFuture future1 = channel.write(message1);
ChannelFuture future2 = channel.write(message2);
ChannelFuture combinedFuture = channel.newPromise();
ChannelFutureListener listener = new ChannelFutureListener() {
private int remaining = 2;
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) {
remaining--;
if (remaining == 0) {
if (future1.isSuccess() && future2.isSuccess()) {
combinedFuture.setSuccess();
} else {
combinedFuture.setFailure(new Exception("At least one operation failed"));
}
}
}
};
future1.addListener(listener);
future2.addListener(listener);2. 性能调优实战
2.1 EventLoopGroup线程数优化
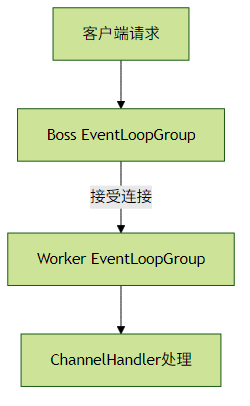
配置建议:
Boss Group:通常1-2个线程足够(除非需要处理数万并发连接)
// 主从Reactor线程模型 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); // 接收连接 EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); // 默认CPU核心数*2Worker Group:
- 计算密集型:CPU核心数+1
- I/O密集型:CPU核心数*2
- 混合型:通过压测确定最佳值
关键参数:
// 在ServerBootstrap中配置
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024) // 连接队列大小
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true) // 保持连接2.2 ByteBuf分配策略
内存池配置:
// 启用内存池(默认已启用)
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT);不同场景建议:
高吞吐量服务:
// 使用直接内存,减少拷贝 .option(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, new PooledByteBufAllocator(true))低延迟服务:
// 调整内存池参数 PooledByteBufAllocator allocator = new PooledByteBufAllocator( true, // preferDirect 16, // nHeapArena 16, // nDirectArena 8192, // pageSize 11, // maxOrder 64, // tinyCacheSize 256, // smallCacheSize 1024 // normalCacheSize );
内存泄漏检测:
// 添加内存泄漏检测handler
pipeline.addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
// 或启动参数添加
-Dio.netty.leakDetection.level=PARANOID3. 故障排查技巧
3.1 日志增强
推荐配置:
// 在pipeline中添加日志handler
pipeline.addFirst("logging", new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
// 或者单独配置Netty日志
<logger name="io.netty" level="DEBUG"/>日志分析要点:
- 关注
WARN和ERROR级别日志 - 特别留意
LEAK关键字(内存泄漏提示) - 异常堆栈中的
ChannelHandler名称定位问题组件
3.2 异常处理最佳实践
全局异常捕获:
public class ExceptionHandler extends ChannelDuplexHandler {
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
if (cause instanceof IOException) {
// 网络异常,通常直接关闭连接
ctx.close();
} else if (cause instanceof DecoderException) {
// 编解码异常,可能返回错误响应
ctx.writeAndFlush(new ErrorResponse("Protocol error"));
} else {
// 其他未处理异常
logger.error("Unexpected error", cause);
ctx.close();
}
}
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) {
ctx.write(msg, promise.addListener(future -> {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
// 写操作异常处理
logger.warn("Write failed", future.cause());
}
}));
}
}常见异常处理:
- ChannelException:检查网络连接和防火墙
- DecoderException:验证数据格式和编解码器
- TimeoutException:调整超时参数或检查网络延迟
- OutOfMemoryError:检查内存泄漏或调整堆大小
总结对比表
| 特性 | 关键配置 | 推荐值 | 监控指标 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 线程模型 | bossGroup线程数 | 1-2 | 连接接受延迟 |
| workerGroup线程数 | CPU核心数*2 | 任务队列积压 | |
| 内存分配 | allocator类型 | PooledByteBufAllocator | 直接内存使用量 |
| preferDirect | true(高性能)/false(低延迟) | GC频率 | |
| 异常处理 | exceptionCaught实现 | 分级处理 | 异常发生频率 |
| 日志级别 | LoggingHandler | DEBUG(开发)/INFO(生产) | 错误日志量 |
最终建议:
- 生产环境务必配置完善的监控(如Prometheus+Granfa)
- 定期进行压力测试,观察不同参数下的性能表现
- 建立异常处理规范,避免随意吞没异常
- 关键操作添加超时控制,防止无限等待
评论已关闭