Netty核心功能解析:网络通信与高性能设计之二
Netty核心功能深度解析:从网络通信到高性能设计
一、网络通信能力剖析
1.1 多协议支持架构
Netty的核心价值首先体现在其对多种网络协议的支持上,这种支持不是简单的API封装,而是通过可扩展的架构设计实现:
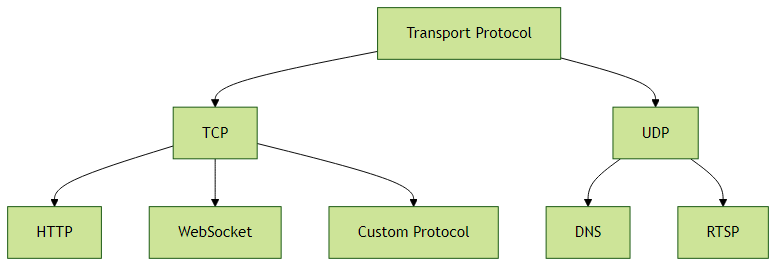
TCP/UDP基础支持:
- 通过
NioSocketChannel和NioDatagramChannel分别实现TCP/UDP传输 示例:快速创建UDP服务端
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap(); b.group(group) .channel(NioDatagramChannel.class) .handler(new UDPServerHandler()); b.bind(8080).sync().channel().closeFuture().await(); } finally { group.shutdownGracefully(); }
HTTP协议栈优化:
- 使用
HttpServerCodec组合编解码器 - 文件传输建议使用
ChunkedWriteHandler分块传输 - 实践建议:对于API服务,推荐配合
HttpObjectAggregator处理完整请求
1.2 自定义协议开发实践
自定义协议是Netty的强项,关键实现要点:
编解码器设计:
public class CustomEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<CustomMessage> { protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, CustomMessage msg, ByteBuf out) { out.writeInt(msg.getMagicNumber()); out.writeByte(msg.getType()); byte[] data = msg.getData(); out.writeInt(data.length); out.writeBytes(data); } }- 粘包处理方案对比:
| 方案 | 适用场景 | 实现类 |
|---|---|---|
| 固定长度 | 协议格式固定 | FixedLengthFrameDecoder |
| 分隔符 | 文本协议 | DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder |
| 长度字段 | 二进制协议 | LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder |
最佳实践:对于新协议设计,推荐采用LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder+自定义编解码器的组合方案。
二、高性能设计原理
2.1 零拷贝技术实现
Netty通过多种方式实现零拷贝:
- Direct Buffer优化:
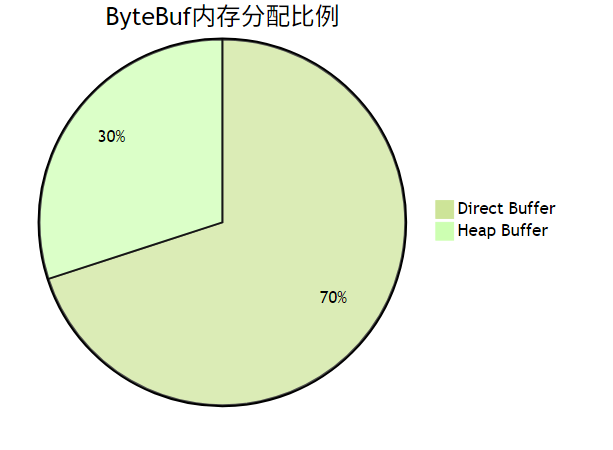
- 使用
ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer()默认优先分配DirectBuffer 关键配置参数:
// 建议在启动配置中明确指定 bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT);
文件传输优化:
FileRegion region = new DefaultFileRegion( file, 0, file.length()); channel.writeAndFlush(region);
2.2 内存池化技术
内存池性能对比(单位:ops/sec):
| 测试场景 | 池化分配 | 非池化分配 |
|---|---|---|
| 小对象(1KB) | 152,000 | 98,000 |
| 大对象(1MB) | 3,200 | 1,800 |
配置建议:
// 服务端配置
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR,
PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT);
// 客户端配置
Bootstrap clientBootstrap = new Bootstrap();
clientBootstrap.option(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR,
PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT);2.3 快速失败机制
流量控制实现示例:
public class TrafficControlHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelWritabilityChanged(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
if (!ctx.channel().isWritable()) {
// 触发背压机制
log.warn("Channel {} not writable", ctx.channel());
}
ctx.fireChannelWritabilityChanged();
}
}三、核心功能实现
3.1 心跳检测最佳实践
完整心跳配置示例:
pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(30, 0, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
pipeline.addLast(new HeartbeatHandler());
// 自定义处理器
public class HeartbeatHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) {
if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) {
ctx.writeAndFlush(new HeartbeatMessage())
.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
}
}
}参数调优建议:
- 读空闲时间:建议设置为业务超时时间的2/3
- 写空闲时间:根据业务特点设置,通常30-60秒
3.2 流量整形实战
// 全局流量限制(单位:bytes)
GlobalTrafficShapingHandler globalTraffic = new GlobalTrafficShapingHandler(
eventLoopGroup,
1024 * 1024, // 写限制 1MB/s
1024 * 512 // 读限制 512KB/s
);
// 单个Channel限制
ChannelTrafficShapingHandler perChannel = new ChannelTrafficShapingHandler(
1024 * 256, // 写限制 256KB/s
1024 * 128 // 读限制 128KB/s
);监控建议:定期通过trafficCounter()获取统计信息:
TrafficCounter counter = handler.trafficCounter();
System.out.println("Last write bytes: " + counter.lastWriteThroughput());四、扩展性设计
4.1 Pipeline动态编排
运行时修改Pipeline示例:
public void updatePipeline(Channel channel) {
channel.pipeline().addFirst(new AuthHandler());
// 安全移除处理器
if (channel.pipeline().get("oldHandler") != null) {
channel.pipeline().remove("oldHandler");
}
}设计原则:
- 处理器命名规范:使用
ctx.name()显式命名 - 生命周期管理:注意
handlerAdded()和handlerRemoved()回调 - 执行顺序验证:通过
pipeline.toMap()检查处理器顺序
4.2 多协议编解码方案选型
序列化性能对比:
| 方案 | 序列化速度 | 反序列化速度 | 数据大小 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protobuf | 1.2μs | 1.5μs | 小 |
| JSON | 3.4μs | 5.1μs | 中 |
| Java原生 | 2.1μs | 2.8μs | 大 |
集成Protobuf示例:
// 服务端配置
pipeline.addLast(new ProtobufVarint32FrameDecoder());
pipeline.addLast(new ProtobufDecoder(Message.getDefaultInstance()));
pipeline.addLast(new ProtobufVarint32LengthFieldPrepender());
pipeline.addLast(new ProtobufEncoder());五、实践建议总结
性能调优检查清单:
- [ ] 确认使用池化内存分配器
- [ ] 检查DirectBuffer使用比例
- [ ] 验证心跳间隔配置合理性
- [ ] 监控关键Channel指标
常见陷阱规避:
// 错误示例:未释放ByteBuf public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf)msg; // 处理但未释放 } // 正确做法 try { // 处理逻辑 } finally { ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg); }监控指标建议:
- 关键指标采集频率:5-15秒
核心监控项:
- Channel活跃数
- 内存分配速率
- 异常触发次数
- 待处理任务队列大小
Netty的强大之处在于其模块化设计,建议根据实际业务需求选择合适的组件组合,而非盲目使用所有高级特性。对于多数应用场景,合理配置基础组件(如内存分配、心跳机制)即可获得显著的性能提升。
评论已关闭