Netty整合实践:RPC、微服务与消息队列
Netty与其他技术整合实践:RPC、微服务与消息队列
Netty作为高性能网络通信框架,在现代分布式系统中常与其他核心技术深度整合。本文将重点剖析Netty在RPC框架、微服务架构和消息队列中的典型应用场景与实现方案。
一、作为RPC框架的底层通信基石
1.1 在Dubbo/gRPC中的应用
主流RPC框架普遍采用Netty作为通信层实现,其优势在于:
- 协议扩展性:通过
ChannelPipeline灵活组装编解码器 - 连接管理:内置心跳检测、断线重连机制
- 性能保障:零拷贝和内存池降低GC压力
Dubbo集成示例:
// Dubbo使用NettyTransporter创建服务器
public class NettyTransporter implements Transporter {
public Server bind(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) {
return new NettyServer(url, handler);
}
}
// NettyServer启动核心代码
public class NettyServer extends AbstractServer {
protected void doOpen() {
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast("decoder", new DubboDecoder())
.addLast("encoder", new DubboEncoder())
.addLast("handler", nettyHandler);
}
});
}
}1.2 协议设计要点
消息格式:通常采用Header+Body结构
// 自定义协议示例 public class RpcProtocol { private short magic = 0xCAFE; // 魔数 private int length; // 消息长度 private byte serialization; // 序列化类型 private byte[] payload; // 实际数据 }- 序列化选择:推荐Protobuf/Kryo等高效方案
- 粘包处理:使用
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder
实践建议:
- 保持协议版本兼容性
- 关键操作添加请求超时控制
- 生产环境开启内存泄漏检测
二、微服务架构中的Netty集成
2.1 与Spring Boot深度整合
自定义启动方案:
@Configuration
public class NettyServerConfig {
@Bean(name = "nettyServer")
public NettyServerBootstrap nettyServerBootstrap() {
return new NettyServerBootstrap(8080);
}
}
public class NettyServerBootstrap implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
private EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
private EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new WebSocketServerInitializer());
ChannelFuture future = b.bind(port).addListener(f -> {
if (f.isSuccess()) {
log.info("Netty started on port: {}", port);
}
});
}
}2.2 服务治理集成
- 服务注册发现:连接ZooKeeper/Nacos
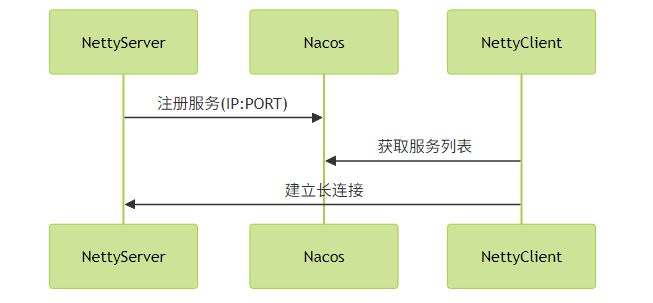
健康检查:通过
IdleStateHandler实现心跳pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(60, 0, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); pipeline.addLast(new HeartbeatHandler());
性能优化点:
- 微服务间连接建议使用EPOLL传输模式(Linux环境)
- 合理设置
SO_BACKLOG应对突发流量 - 采用连接池管理重要服务通道
三、消息队列通信层实现
3.1 RocketMQ Remoting模块分析
RocketMQ的Remoting模块完全基于Netty实现:
// NettyRemotingServer初始化
public class NettyRemotingServer extends NettyRemotingAbstract {
public void start() {
this.serverBootstrap.group(this.eventLoopGroupBoss, this.eventLoopGroupSelector)
.channel(useEpoll() ? EpollServerSocketChannel.class : NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new NettyServerHandler())
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast(defaultEventExecutorGroup,
new NettyEncoder(),
new NettyDecoder(),
new IdleStateHandler(0, 0, nettyServerConfig.getServerChannelMaxIdleTimeSeconds()),
new NettyConnectManageHandler(),
new NettyServerHandler());
}
});
}
}3.2 关键设计决策
- IO线程与业务线程分离:
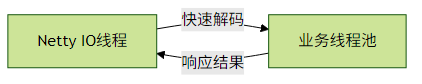
- 批量消息处理:使用
CompositeByteBuf合并小包 - 流量控制:通过
ChannelTrafficShapingHandler限速
高可用实践:
- 消息重试机制需考虑幂等性
- 客户端实现故障自动转移
- 重要通道启用SSL双向认证
四、整合架构建议
线程模型规划:
场景 推荐配置 API网关 主从多线程(Boss:1, Worker:CPU*2) 内部服务通信 共享EventLoopGroup 消息队列Broker 独立业务线程池 监控指标埋点:
// 使用Micrometer暴露指标 public class NettyMetrics { void registerMetrics(EventLoopGroup group) { Gauge.builder("netty.thread.active", () -> group.children().stream() .filter(e -> !e.inEventLoop()) .count()) .register(meterRegistry); } }常见避坑指南:
- 避免在ChannelHandler中阻塞操作
- 谨慎使用
@Sharable注解 - 序列化协议需考虑向前兼容
Netty与其他技术的整合既需要深入理解其线程模型和内存管理机制,也要根据具体场景进行针对性优化。建议在实际项目中通过压测确定最优参数配置,并建立完善的监控体系。
评论已关闭