Netty性能优化实战:线程模型与内存管理技巧
Netty性能优化与调优实战指南
一、线程模型优化
1. 主从Reactor线程配置
Netty默认采用主从Reactor线程模型:
- 主Reactor(bossGroup):处理连接请求
- 从Reactor(workerGroup):处理I/O读写
// 推荐配置示例
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); // 通常1个线程足够
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); // 默认CPU核心数*2
// 特殊场景调整
EventLoopGroup customGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(16,
new DefaultThreadFactory("netty-worker", true)); // 自定义线程工厂实践建议:
- 生产环境bossGroup通常设置为1(单端口监听场景)
- workerGroup线程数建议为CPU核心数的1.5-2倍
- 高并发场景可考虑增加线程数,但需注意上下文切换开销
2. 业务线程池隔离
避免耗时业务阻塞I/O线程:
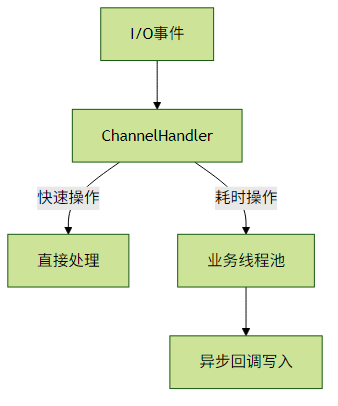
// 业务线程池配置
ExecutorService businessExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2,
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
// ChannelHandler中使用
channel.pipeline().addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String>() {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) {
businessExecutor.execute(() -> {
// 耗时业务处理
String result = processBusiness(msg);
ctx.writeAndFlush(result);
});
}
});二、内存管理优化
1. ByteBuf分配策略
| 分配类型 | 特点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| 池化(Pooled) | 减少内存分配/回收开销 | 高并发、频繁分配场景 |
| 非池化(Unpooled) | 简单直接 | 测试环境、低频使用 |
| Direct Buffer | 零拷贝、堆外内存 | 需要减少内存拷贝的场景 |
| Heap Buffer | JVM堆内存 | 需要频繁访问数据的场景 |
推荐配置:
// 服务端引导类配置
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT);
bootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR, new AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator());2. 内存泄漏检测
Netty提供四级检测机制:
- DISABLED:关闭检测
- SIMPLE:简单采样检测(默认)
- ADVANCED:高级采样检测
- PARANOID:全量检测(性能影响大)
// 启动参数设置检测级别
-Dio.netty.leakDetection.level=ADVANCED常见泄漏场景:
- 未调用
ByteBuf.release() - handler未正确覆盖
handlerRemoved() - 未处理
ChannelFuture的失败情况
三、关键参数调优
1. Socket参数配置
| 参数 | 建议值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| SO_BACKLOG | 1024 | 等待连接队列大小 |
| TCP_NODELAY | true | 禁用Nagle算法 |
| SO_REUSEADDR | true | 端口复用 |
| SO_KEEPALIVE | true | 启用TCP保活 |
| SO_RCVBUF/SO_SNDBUF | 动态调整 | 根据带宽时延积(BDP)计算 |
// 典型配置示例
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024)
.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);2. 其他关键参数
// 连接超时设置
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 3000);
// 写缓冲区水位线
bootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.WRITE_BUFFER_WATER_MARK,
new WriteBufferWaterMark(32 * 1024, 64 * 1024));四、零拷贝技术应用
1. FileRegion传输文件
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
FileRegion region = new DefaultFileRegion(
in.getChannel(), 0, file.length());
channel.writeAndFlush(region).addListener(future -> {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
in.close();
}
});2. CompositeByteBuf合并缓冲区
ByteBuf header = Unpooled.wrappedBuffer("Header".getBytes());
ByteBuf body = Unpooled.wrappedBuffer("Body".getBytes());
CompositeByteBuf composite = Unpooled.compositeBuffer();
composite.addComponents(true, header, body); // true表示自动增加writerIndex
channel.writeAndFlush(composite);五、性能调优检查清单
线程模型
- [ ] 确认bossGroup线程数合理(通常1个)
- [ ] workerGroup线程数与CPU核心数匹配
- [ ] 耗时操作已卸载到业务线程池
内存管理
- [ ] 使用池化分配器(PooledByteBufAllocator)
- [ ] 合理设置内存检测级别
- [ ] 所有ByteBuf都正确释放
网络参数
- [ ] SO_BACKLOG设置合理值
- [ ] 禁用Nagle算法(TCP_NODELAY=true)
- [ ] 根据网络条件调整缓冲区大小
监控指标
- [ ] 监控I/O线程利用率
- [ ] 跟踪内存分配/释放情况
- [ ] 记录关键操作的延迟分布
通过以上优化措施,Netty应用可以达到百万级QPS的性能表现。实际调优时需要结合具体业务场景和压力测试结果进行针对性调整。
评论已关闭