Seata事务模式实战:AT/TCC/SAGA配置指南
Seata常规用法与配置实战指南
本文将深入讲解Seata的三种主要事务模式(AT/TCC/SAGA)的使用方法,以及与微服务框架的集成实践。
一、AT模式使用
1. 依赖引入
<dependency>
<groupId>io.seata</groupId>
<artifactId>seata-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>最新版本</version>
</dependency>2. 基础配置
seata:
enabled: true
application-id: order-service
tx-service-group: my_tx_group # 事务分组需与seata-server配置一致
service:
vgroup-mapping:
my_tx_group: default # 映射到seata-server集群
config:
type: nacos # 配置中心类型
registry:
type: nacos # 注册中心类型
store:
mode: db # 事务日志存储模式(db/file/redis)
db:
datasource: druid
db-type: mysql
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/seata
user: root
password: root3. 注解使用
@Service
public class OrderService {
@GlobalTransactional(timeoutMills = 300000, name = "createOrder")
public void createOrder(Order order) {
// 1. 扣减库存
storageFeignClient.deduct(order.getProductId(), order.getCount());
// 2. 创建订单
orderMapper.insert(order);
// 3. 扣减账户余额
accountFeignClient.debit(order.getUserId(), order.getMoney());
}
}实践建议:
- 超时时间(timeoutMills)应根据业务链路的实际耗时合理设置
- 全局事务入口方法建议添加事务名称(name)便于问题排查
- 避免在全局事务方法中进行耗时操作(如文件IO)
二、TCC模式实现
1. 接口定义
@LocalTCC
public interface AccountTccService {
@TwoPhaseBusinessAction(name = "debit", commitMethod = "confirm", rollbackMethod = "cancel")
boolean tryDebit(@BusinessActionContextParameter(paramName = "userId") String userId,
@BusinessActionContextParameter(paramName = "money") BigDecimal money);
boolean confirm(BusinessActionContext context);
boolean cancel(BusinessActionContext context);
}2. 业务实现
@Service
public class AccountTccServiceImpl implements AccountTccService {
@Autowired
private AccountFreezeMapper freezeMapper;
@Override
public boolean tryDebit(String userId, BigDecimal money) {
// 检查账户余额
Account account = accountMapper.selectById(userId);
if (account.getBalance().compareTo(money) < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("余额不足");
}
// 冻结金额
AccountFreeze freeze = new AccountFreeze();
freeze.setUserId(userId);
freeze.setFreezeMoney(money);
freeze.setState(AccountFreezeState.TRY);
freezeMapper.insert(freeze);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean confirm(BusinessActionContext context) {
// 扣减实际金额
String userId = (String) context.getActionContext("userId");
BigDecimal money = (BigDecimal) context.getActionContext("money");
accountMapper.reduceBalance(userId, money);
// 删除冻结记录
freezeMapper.delete(new LambdaQueryWrapper<AccountFreeze>()
.eq(AccountFreeze::getUserId, userId)
.eq(AccountFreeze::getState, AccountFreezeState.TRY));
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean cancel(BusinessActionContext context) {
// 释放冻结金额
String userId = (String) context.getActionContext("userId");
freezeMapper.delete(new LambdaQueryWrapper<AccountFreeze>()
.eq(AccountFreeze::getUserId, userId)
.eq(AccountFreeze::getState, AccountFreezeState.TRY));
return true;
}
}实践建议:
- Try阶段应预留资源,Confirm/Cancel阶段必须实现幂等性
- 业务上下文(BusinessActionContext)可用于跨阶段参数传递
- 建议每个TCC服务单独建表记录资源预留状态
三、SAGA模式应用
1. 状态机定义(JSON)
{
"name": "orderProcess",
"steps": [
{
"name": "createOrder",
"service": "orderService",
"serviceMethod": "create",
"compensateService": "orderService",
"compensateMethod": "cancel"
},
{
"name": "reserveInventory",
"service": "inventoryService",
"serviceMethod": "reserve",
"compensateService": "inventoryService",
"compensateMethod": "release"
},
{
"name": "processPayment",
"service": "paymentService",
"serviceMethod": "pay",
"compensateService": "paymentService",
"compensateMethod": "refund"
}
]
}2. 状态机执行
StateMachineEngine stateMachineEngine = StateMachineEngineHolder.getStateMachineEngine();
Map<String, Object> startParams = new HashMap<>();
startParams.put("orderParams", orderDto);
startParams.put("inventoryParams", inventoryReq);
StateMachineInstance instance = stateMachineEngine.start(
"orderProcess",
null,
startParams);实践建议:
- 适用于业务流程长、需要人工干预的场景
- 补偿服务必须实现幂等且可重试
- 建议配合可视化工具设计状态机流程
四、与微服务框架集成
1. Spring Cloud集成
@FeignClient(name = "account-service")
public interface AccountFeignClient {
@PostMapping("/account/debit")
Boolean debit(@RequestParam("userId") String userId,
@RequestParam("money") BigDecimal money);
}
// 自动传递XID的RestTemplate配置
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
restTemplate.setInterceptors(Collections.singletonList(
new SeataRestTemplateInterceptor()));
return restTemplate;
}2. Dubbo集成
@Service(version = "1.0.0", interfaceClass = AccountService.class)
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Override
@GlobalTransactional
public boolean debit(String userId, BigDecimal money) {
// 业务实现
}
}
// 消费者调用
@Reference(version = "1.0.0")
private AccountService accountService;实践建议:
- Feign/RestTemplate需确保Seata拦截器正确配置
- Dubbo服务建议使用1.4.2+版本以获得最佳兼容性
- 跨服务调用时避免使用@Transactional与@GlobalTransactional混用
五、模式选型建议
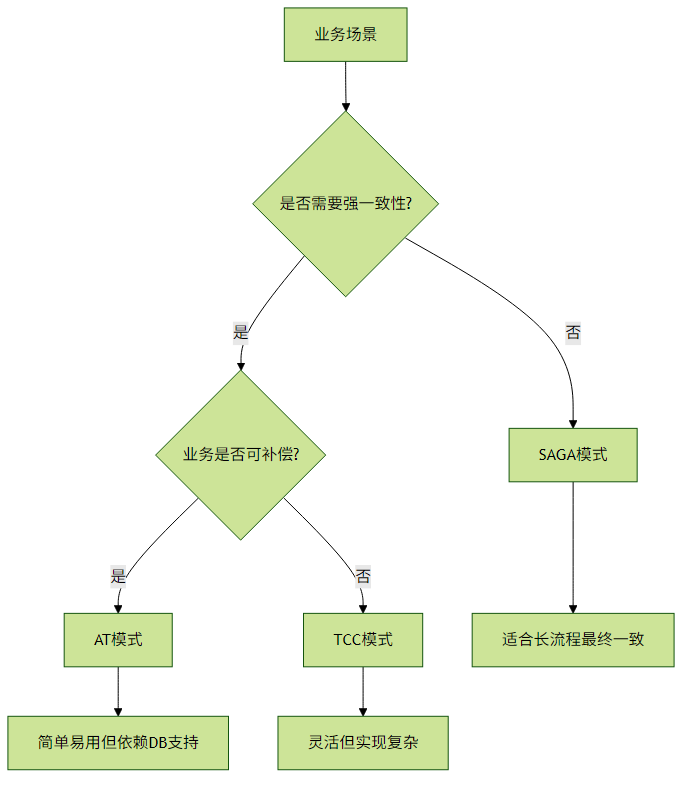
选型原则:
- AT模式:适合大多数简单场景,对业务侵入小
- TCC模式:需要强一致性且业务可补偿的场景
- SAGA模式:业务流程长且可接受最终一致性的场景
通过以上配置和示例,开发者可以快速在项目中集成Seata的分布式事务能力。建议根据实际业务需求选择合适的事务模式,并在测试环境充分验证事务行为。
评论已关闭