MQTT物联网平台接入指南:云平台规范与数据交互
物联网平台MQTT深度集成指南:云平台接入规范与数据交互模式
一、主流云平台MQTT接入规范对比
1. 阿里云物联网平台接入要点
连接参数:
// Java示例:Paho客户端连接阿里云 MqttConnectOptions options = new MqttConnectOptions(); options.setUserName("deviceName&productKey"); options.setPassword("deviceSecret".toCharArray()); options.setCleanSession(true); options.setKeepAliveInterval(90);主题规范:
- 上行:
/sys/{productKey}/{deviceName}/thing/event/property/post - 下行:
/sys/{productKey}/{deviceName}/thing/service/property/set
- 上行:
特殊要求:
- 必须使用TLS 1.2加密
- 设备心跳间隔建议60-300秒
- 单个消息最大256KB
2. 华为云IoT接入差异
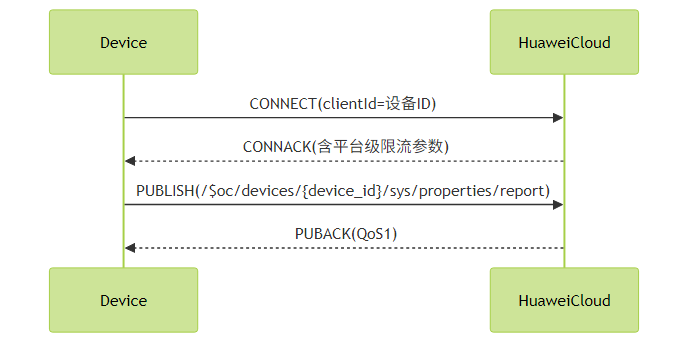
关键区别:
- 设备ID直接作为clientId
- 主题前缀使用
/$oc/命名空间 - 支持MQTT 5.0特性(如原因码)
实践建议:开发多平台适配层时,建议抽象出以下接口:
public interface CloudPlatformAdapter {
void configureTopicTemplate();
MqttConnectOptions buildConnectionOptions();
void processPlatformSpecificMessage(MqttMessage message);
}二、设备影子(Device Shadow)交互模式解析
1. 双通道同步机制
设备端状态上报:
{ "state": { "reported": { "temperature": 25.6, "fanSpeed": "HIGH" } } }服务端期望状态:
{ "state": { "desired": { "ledColor": "BLUE" } }, "version": 42 }
2. 冲突解决策略
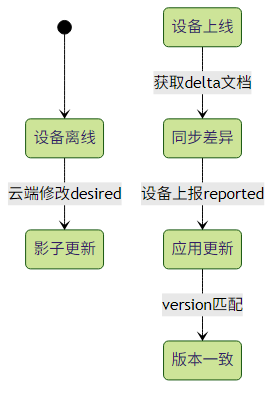
最佳实践:
- 设备启动时先获取完整影子文档
- 处理
desired与reported的差异(delta) - 实现版本号校验(避免旧数据覆盖)
三、物模型(TSL)数据格式转换
1. 标准物模型结构示例
{
"properties": [
{
"identifier": "temperature",
"dataType": {
"type": "float",
"min": "-20",
"max": "80",
"unit": "℃"
}
}
],
"events": {
"error": {
"outputData": [
{
"identifier": "errorCode",
"dataType": "int"
}
]
}
}
}2. 协议转换层实现
// 设备原始数据转换示例
public class TslConverter {
public static JsonNode convertToTslFormat(DeviceRawData raw) {
ObjectNode node = JsonNodeFactory.instance.objectNode();
node.put("id", UUID.randomUUID().toString());
node.put("version", "1.0");
ObjectNode params = node.putObject("params");
params.put(raw.getFieldName(), raw.getValue());
return node;
}
}关键处理逻辑:
- 数据类型校验(根据TSL定义)
- 单位换算(如华氏度转摄氏度)
- 非法值过滤(超出min/max范围)
四、实战:端到端数据流示例
1. 温度传感器上报流程
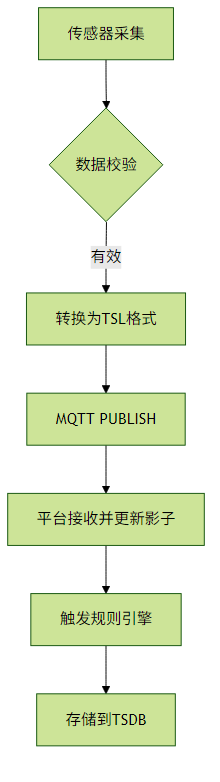
2. 服务端控制指令下发
// 订阅控制主题示例
public void subscribeControlTopic() {
client.subscribe("/shadow/update/accepted", (topic, message) -> {
ShadowDocument doc = parseShadow(message.getPayload());
if(doc.hasDelta()) {
applyDeviceControl(doc.getDesired());
updateReportedState(doc.getVersion());
}
});
}五、性能优化与安全建议
连接管理:
- 使用持久会话减少重连开销
- 合理设置KeepAlive(移动网络建议120秒)
消息压缩:
// 使用Gzip压缩payload示例 byte[] compressPayload(byte[] input) throws IOException { ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); GZIPOutputStream gzip = new GZIPOutputStream(bos); gzip.write(input); gzip.close(); return bos.toByteArray(); }安全加固:
- 定期轮换设备证书
- 实现Topic级别的ACL控制
- 禁用低版本TLS(只允许TLS 1.2+)
典型问题排查清单:
- 连接失败:检查三元组(ProductKey/DeviceName/DeviceSecret)
- 订阅无效:确认Topic权限和通配符使用
- 消息丢失:调整QoS等级(关键数据用QoS1)
- 同步延迟:检查影子文档版本冲突
通过以上规范与模式,开发者可快速实现设备与云平台的高效、可靠集成。实际项目中建议结合平台SDK(如阿里云Link Kit)进一步简化开发流程。
评论已关闭