JavaScript进阶:设计模式、安全与工具链详解
JavaScript 核心进阶:设计模式、安全与现代工具链
一、设计模式
1. 工厂模式
工厂模式是一种创建型模式,用于封装对象的创建过程。
class Car {
constructor(make, model) {
this.make = make;
this.model = model;
}
}
class CarFactory {
createCar(type) {
switch(type) {
case 'sedan':
return new Car('Toyota', 'Camry');
case 'suv':
return new Car('Honda', 'CR-V');
default:
throw new Error('Unknown car type');
}
}
}
const factory = new CarFactory();
const myCar = factory.createCar('suv');实践建议:当创建逻辑复杂或需要根据不同条件创建不同对象时使用工厂模式。
2. 单例模式
确保一个类只有一个实例,并提供全局访问点。
class Database {
constructor() {
if (Database.instance) {
return Database.instance;
}
this.connection = 'Connected to DB';
Database.instance = this;
}
}
const db1 = new Database();
const db2 = new Database();
console.log(db1 === db2); // true实践建议:适用于数据库连接、配置管理等需要全局唯一实例的场景。
3. 观察者模式
定义对象间的一对多依赖关系,当一个对象状态改变时,所有依赖它的对象都会得到通知。
class Subject {
constructor() {
this.observers = [];
}
subscribe(observer) {
this.observers.push(observer);
}
unsubscribe(observer) {
this.observers = this.observers.filter(obs => obs !== observer);
}
notify(data) {
this.observers.forEach(observer => observer.update(data));
}
}
class Observer {
update(data) {
console.log('Received data:', data);
}
}
const subject = new Subject();
const observer1 = new Observer();
subject.subscribe(observer1);
subject.notify('Hello World!');实践建议:适用于事件处理系统、状态管理等需要解耦的场景。
二、安全相关
1. XSS防御
跨站脚本攻击(XSS)防御措施:
// 转义HTML
function escapeHtml(unsafe) {
return unsafe
.replace(/&/g, "&")
.replace(/</g, "<")
.replace(/>/g, ">")
.replace(/"/g, """)
.replace(/'/g, "'");
}
// 使用textContent而不是innerHTML
document.getElementById('output').textContent = userInput;2. CSRF防御
跨站请求伪造(CSRF)防御措施:
// 服务端生成并返回CSRF令牌
fetch('/csrf-token')
.then(res => res.json())
.then(data => {
const csrfToken = data.token;
// 在后续请求中包含令牌
fetch('/api/data', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'X-CSRF-Token': csrfToken
},
body: JSON.stringify({ /* data */ })
});
});3. Content Security Policy (CSP)
通过HTTP头或meta标签设置:
<meta http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy"
content="default-src 'self'; script-src 'self' https://trusted.cdn.com;">实践建议:
- 对所有用户输入进行验证和转义
- 实施最小权限原则
- 定期更新依赖库以修复安全漏洞
三、现代工具链
1. Webpack配置示例
// webpack.config.js
const path = require('path');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
filename: 'bundle.[contenthash].js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
clean: true
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.js$/,
exclude: /node_modules/,
use: {
loader: 'babel-loader',
options: {
presets: ['@babel/preset-env']
}
}
},
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: ['style-loader', 'css-loader']
}
]
},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index.html'
})
]
};2. Babel配置
// .babelrc
{
"presets": [
["@babel/preset-env", {
"targets": {
"browsers": ["last 2 versions", "not dead"]
},
"useBuiltIns": "usage",
"corejs": 3
}]
],
"plugins": ["@babel/plugin-transform-runtime"]
}3. ESLint配置
// .eslintrc.js
module.exports = {
env: {
browser: true,
es2021: true
},
extends: ['eslint:recommended', 'plugin:prettier/recommended'],
parserOptions: {
ecmaVersion: 'latest',
sourceType: 'module'
},
rules: {
'no-console': 'warn',
'no-unused-vars': 'error',
'prettier/prettier': 'error'
}
};实践建议:
- 使用Webpack进行代码分割和懒加载优化性能
- 配置Babel兼容目标浏览器
- 在CI/CD流程中加入ESLint检查
四、框架特性
1. React Hooks核心用法
import { useState, useEffect, useMemo, useCallback } from 'react';
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
// 相当于componentDidMount和componentDidUpdate
useEffect(() => {
document.title = `Count: ${count}`;
// 清理函数,相当于componentWillUnmount
return () => {
document.title = 'React App';
};
}, [count]); // 依赖数组
// 记忆化计算结果
const doubled = useMemo(() => count * 2, [count]);
// 记忆化函数
const increment = useCallback(() => {
setCount(c => c + 1);
}, []);
return (
<div>
<p>Count: {count}, Doubled: {doubled}</p>
<button onClick={increment}>Increment</button>
</div>
);
}2. Vue响应式原理示例
// Vue 3 Composition API
import { ref, reactive, computed, watchEffect } from 'vue';
const state = reactive({
count: 0,
message: 'Hello'
});
const double = computed(() => state.count * 2);
watchEffect(() => {
console.log(`Count changed to: ${state.count}`);
});
function increment() {
state.count++;
}
// 在模板中使用
// <button @click="increment">{{ count }} ({{ double }})</button>响应式原理简析:
Vue 3使用Proxy实现响应式,基本流程如下:
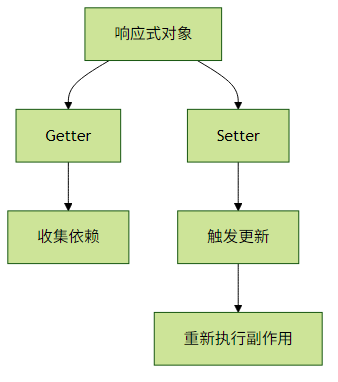
实践建议:
- 合理使用Hooks/Composition API组织组件逻辑
- 避免在渲染函数中进行昂贵计算,使用useMemo/computed
- 理解框架响应式原理有助于性能优化
总结
JavaScript生态系统不断发展,掌握这些核心概念能帮助开发者:
- 编写更可维护的代码(设计模式)
- 构建更安全的应用程序(安全实践)
- 利用现代工具提高开发效率(工具链)
- 深入理解主流框架的工作原理(框架特性)
持续关注ECMAScript新特性和社区最佳实践,将有助于保持技术竞争力。
评论已关闭