JavaScript核心用法指南:数组与字符串操作精要
JavaScript 常规用法精要指南
JavaScript 作为现代 Web 开发的基石语言,其常规用法是每位开发者必须掌握的技能。本文将深入浅出地讲解 JavaScript 在日常开发中最常用的七大核心功能。
一、数组操作:数据处理的核心
数组是 JavaScript 中最常用的数据结构之一,掌握其操作方法能极大提升开发效率。
1. 增删改查基础操作
// 增加元素
const fruits = ['apple'];
fruits.push('banana'); // 末尾添加 ['apple', 'banana']
fruits.unshift('orange'); // 开头添加 ['orange', 'apple', 'banana']
// 删除元素
fruits.pop(); // 删除末尾 'banana',返回 ['orange', 'apple']
fruits.shift(); // 删除开头 'orange',返回 ['apple']
// 修改元素
fruits.splice(1, 0, 'mango'); // 在索引1处插入 'mango',不删除元素
fruits.splice(0, 1, 'pear'); // 替换索引0的元素为 'pear'实践建议:splice 方法功能强大但会修改原数组,在函数式编程中建议优先使用不改变原数组的方法。
2. 数组遍历方法对比
const numbers = [1, 2, 3];
// forEach - 简单遍历
numbers.forEach(num => console.log(num));
// map - 返回新数组
const doubled = numbers.map(num => num * 2);
// for...of - 可中断的遍历
for (const num of numbers) {
if (num > 2) break;
console.log(num);
}性能对比:
| 方法 | 可中断 | 返回新数组 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| forEach | 否 | 否 | 简单遍历 |
| map | 否 | 是 | 数据转换 |
| for...of | 是 | 否 | 需要中断或复杂逻辑遍历 |
3. 数组扁平化处理
const nested = [1, [2, [3]]];
// flat方法
nested.flat(2); // [1, 2, 3]
// flatMap方法(先map后flat)
const sentences = ["Hello world", "Good morning"];
const words = sentences.flatMap(s => s.split(' '));
// ["Hello", "world", "Good", "morning"]二、字符串处理:文本操作的艺术
现代 JavaScript 提供了丰富的字符串操作方法。
1. 模板字符串的高级用法
const user = { name: 'Alice', age: 25 };
// 基本插值
console.log(`User ${user.name} is ${user.age} years old`);
// 标签模板(高级用法)
function highlight(strings, ...values) {
return strings.reduce((result, str, i) =>
`${result}${str}<mark>${values[i] || ''}</mark>`, '');
}
highlight`User ${user.name} is ${user.age} years old`;
// 返回 "User <mark>Alice</mark> is <mark>25</mark> years old"2. 常用字符串方法
const text = "JavaScript is awesome";
// 包含检查
text.includes('Script'); // true
text.startsWith('Java'); // true
// 分割与替换
text.split(' '); // ["JavaScript", "is", "awesome"]
text.replace('awesome', 'powerful'); // "JavaScript is powerful"
// 正则替换
text.replace(/\s/g, '-'); // "JavaScript-is-awesome"三、错误处理:构建健壮应用
良好的错误处理是专业开发的标志。
1. try-catch-finally 模式
function riskyOperation() {
try {
// 可能抛出错误的代码
const data = JSON.parse(maybeInvalidJson);
if (!data.valid) {
throw new Error('Invalid data structure');
}
return data;
} catch (error) {
// 处理已知错误
if (error instanceof SyntaxError) {
console.error('JSON解析错误:', error.message);
} else {
// 重新抛出未知错误
throw error;
}
} finally {
// 无论成功失败都会执行的清理代码
console.log('操作完成');
}
}2. 自定义错误类型
class ValidationError extends Error {
constructor(message, field) {
super(message);
this.name = 'ValidationError';
this.field = field;
this.date = new Date();
}
}
try {
throw new ValidationError('Invalid email', 'email');
} catch (error) {
if (error instanceof ValidationError) {
console.error(`${error.field}验证失败: ${error.message}`);
}
}四、JSON 处理:数据交换的标准
JSON 是现代 Web 应用数据交换的事实标准。
1. 基本序列化与反序列化
const user = {
name: 'Bob',
age: 30,
hobbies: ['coding', 'reading'],
toJSON() { // 自定义序列化行为
return {
name: this.name.toUpperCase(),
age: this.age
};
}
};
// 序列化
const json = JSON.stringify(user);
// '{"name":"BOB","age":30}'
// 反序列化
const parsed = JSON.parse(json, (key, value) => {
// 自定义解析逻辑
return key === 'age' ? value + 1 : value;
});2. 深拷贝实现方案
// 简单深拷贝(有局限性)
function deepClone(obj) {
return JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj));
}
// 完整深拷贝(递归实现)
function completeDeepClone(obj, cache = new WeakMap()) {
if (obj === null || typeof obj !== 'object') return obj;
if (cache.has(obj)) return cache.get(obj);
const clone = Array.isArray(obj) ? [] : {};
cache.set(obj, clone);
for (const key in obj) {
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
clone[key] = completeDeepClone(obj[key], cache);
}
}
return clone;
}五、定时器:异步编程基础
定时器是 JavaScript 异步编程的基础设施。
1. 基本定时器使用
// 单次定时器
const timeoutId = setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Delayed log');
}, 1000);
// 清除定时器
clearTimeout(timeoutId);
// 循环定时器
let counter = 0;
const intervalId = setInterval(() => {
console.log(`Tick ${++counter}`);
if (counter >= 5) clearInterval(intervalId);
}, 500);2. 定时器高级模式
// 链式定时器(替代setInterval)
function delayedLog(message, times) {
let count = 0;
function run() {
console.log(message);
if (++count < times) {
setTimeout(run, 1000);
}
}
setTimeout(run, 1000);
}
// 精确计时(补偿机制)
let start = Date.now();
let expected = start + 1000;
function preciseTimer() {
const drift = Date.now() - expected;
console.log('Drift:', drift, 'ms');
// 业务逻辑...
expected += 1000;
setTimeout(preciseTimer, Math.max(0, 1000 - drift));
}
setTimeout(preciseTimer, 1000);六、正则表达式:强大的模式匹配
正则表达式是处理复杂文本的利器。
1. 基本语法与使用
const regex = /(\d{4})-(\d{2})-(\d{2})/;
const dateStr = '2023-05-15';
// 测试匹配
regex.test(dateStr); // true
// 提取匹配组
const match = dateStr.match(regex);
console.log(match[1]); // "2023"
console.log(match[2]); // "05"
// 替换
dateStr.replace(regex, '$2/$3/$1'); // "05/15/2023"2. 常用正则模式
// 邮箱验证
const emailRegex = /^[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,}$/;
// 密码强度(至少8字符,含大小写和数字)
const passwordRegex = /^(?=.*\d)(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[A-Z]).{8,}$/;
// 提取URL参数
function getQueryParams(url) {
const params = {};
url.replace(/([^?=&]+)=([^&]*)/g, (_, key, value) => {
params[key] = decodeURIComponent(value);
});
return params;
}七、性能优化:流畅用户体验
性能优化是提升用户体验的关键。
1. 防抖与节流实现
// 防抖(最后一次操作后等待)
function debounce(func, wait) {
let timeout;
return function(...args) {
clearTimeout(timeout);
timeout = setTimeout(() => func.apply(this, args), wait);
};
}
// 节流(固定间隔执行)
function throttle(func, limit) {
let inThrottle;
return function(...args) {
if (!inThrottle) {
func.apply(this, args);
inThrottle = true;
setTimeout(() => inThrottle = false, limit);
}
};
}
// 使用示例
window.addEventListener('resize', debounce(() => {
console.log('Resize event handler');
}, 250));2. 虚拟DOM Diff算法核心思想
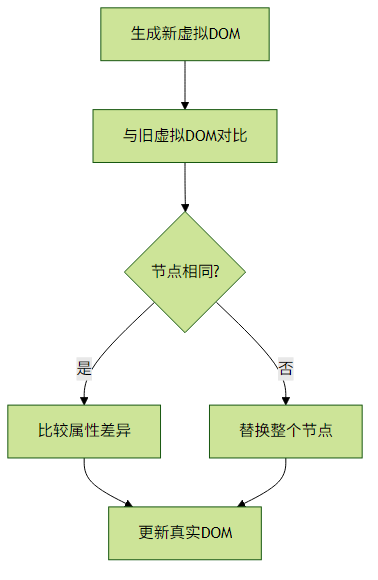
关键优化点:
- 同级比较(不跨层级)
- Key属性优化列表渲染
- 批量DOM更新
// 简化的Diff算法示例
function diff(oldVNode, newVNode) {
if (oldVNode.tag !== newVNode.tag) {
return { type: 'REPLACE', node: newVNode };
}
const patches = {};
const propsDiff = diffProps(oldVNode.props, newVNode.props);
if (propsDiff.length) {
patches.props = propsDiff;
}
const childrenDiff = diffChildren(oldVNode.children, newVNode.children);
if (childrenDiff.length) {
patches.children = childrenDiff;
}
return Object.keys(patches).length ? patches : null;
}总结与最佳实践
- 数组操作:优先使用不改变原数组的方法(如map、filter),需要修改时明确使用splice
- 字符串处理:模板字符串应作为首选,复杂替换考虑正则表达式
- 错误处理:区分可恢复错误和不可恢复错误,自定义错误类型提供更多上下文
- JSON处理:对于敏感数据,考虑实现toJSON方法控制序列化内容
- 定时器:长时间运行的定时器应实现补偿机制避免时间漂移
- 正则表达式:复杂正则应添加注释说明,考虑使用正则测试工具验证
- 性能优化:防抖节流应根据实际场景选择,虚拟DOM优化应配合key属性使用
掌握这些常规用法,你将能够编写出更高效、更健壮的JavaScript代码,为构建复杂Web应用打下坚实基础。
评论已关闭