Webpack高级技巧:自定义插件与动态配置指南
Webpack 高级用法:自定义插件与动态配置
一、自定义 Webpack 插件
概念解析
Webpack 插件是其扩展机制的核心,允许开发者在构建流程的各个生命周期中注入自定义逻辑。与 Loader 处理特定文件不同,插件能介入整个构建过程。
在 Vue CLI 中注入插件
通过 vue.config.js 的 configureWebpack 注入:
const MyPlugin = require('./my-plugin.js');
module.exports = {
configureWebpack: {
plugins: [
new MyPlugin({
// 插件配置
})
]
}
}自定义插件示例
实现一个简单的构建完成通知插件:
class BuildNotifierPlugin {
apply(compiler) {
compiler.hooks.done.tap('BuildNotifier', stats => {
if (!stats.hasErrors()) {
console.log('\x1b[32m%s\x1b[0m', 'Build completed successfully!');
}
});
}
}实践建议
- 生命周期选择:根据需求选择合适的钩子(如
compile、emit、done) - 参数处理:通过插件选项实现可配置性
- 错误处理:确保插件不会导致构建流程中断
二、使用 webpack-merge 合并配置
为什么需要合并
当配置需要根据不同环境动态调整时,直接覆盖会导致配置冗余。webpack-merge 提供智能深度合并能力。
基本用法
const { merge } = require('webpack-merge');
const baseConfig = require('./webpack.base.js');
module.exports = {
configureWebpack: (config) => {
return merge(config, {
// 自定义配置
module: {
rules: [
// 新增规则
]
}
});
}
}合并策略控制
const { mergeWithCustomize, customizeArray } = require('webpack-merge');
const merge = mergeWithCustomize({
customizeArray: customizeArray({
'module.rules': 'prepend' // 将新规则插入数组开头
})
});实践建议
- 环境区分:建立
webpack.dev.js、webpack.prod.js等环境专用配置 - 公共提取:将公共配置抽离到
webpack.common.js - 合并顺序:注意合并顺序影响最终配置
三、动态配置生成
基于环境变量的配置
module.exports = {
configureWebpack: (config) => {
const isProd = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production';
return {
devtool: isProd ? false : 'cheap-module-source-map',
plugins: [
isProd && new CompressionPlugin()
].filter(Boolean)
}
}
}多环境部署方案
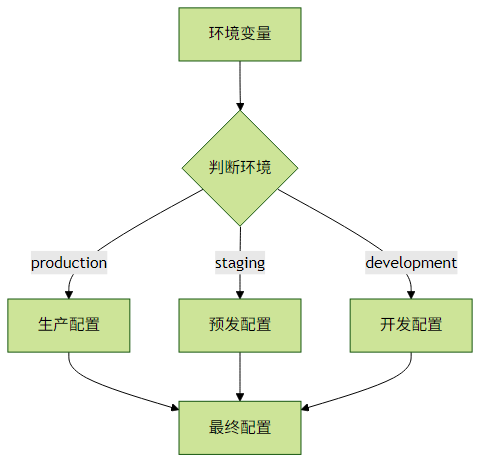
外部参数动态配置
// package.json
"scripts": {
"build:analyz": "vue-cli-service build --mode production --analyz"
}
// vue.config.js
module.exports = {
configureWebpack: (config) => {
if (process.argv.includes('--analyz')) {
config.plugins.push(new BundleAnalyzerPlugin());
}
}
}实践建议
- 配置验证:使用
webpack-validate验证动态生成的配置 - 缓存策略:动态配置可能影响构建缓存,需合理设置缓存键
- 文档记录:为动态参数编写清晰的文档说明
四、综合应用示例
多环境构建配置
// config/proxy.js
module.exports = {
dev: {
'/api': { target: 'http://dev.example.com' }
},
test: {
'/api': { target: 'http://test.example.com' }
}
}
// vue.config.js
const proxyConfig = require('./config/proxy');
const env = process.env.VUE_APP_ENV || 'dev';
module.exports = {
devServer: {
proxy: proxyConfig[env]
},
configureWebpack: {
plugins: [
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env.API_BASE': JSON.stringify(env)
})
]
}
}性能优化配置
module.exports = {
configureWebpack: (config) => {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production') {
return merge(config, {
optimization: {
splitChunks: {
cacheGroups: {
vendors: {
test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]/,
priority: -10
},
common: {
minChunks: 2,
priority: -20,
reuseExistingChunk: true
}
}
}
}
});
}
}
}通过掌握这些高级用法,开发者可以灵活应对各种复杂构建场景,实现高度定制化的前端工程化方案。
评论已关闭