Vue路由配置指南:从基础到高级实践
Vue路由配置与设计:从基础模式到高级实践
一、路由模式解析
Hash模式 vs History模式
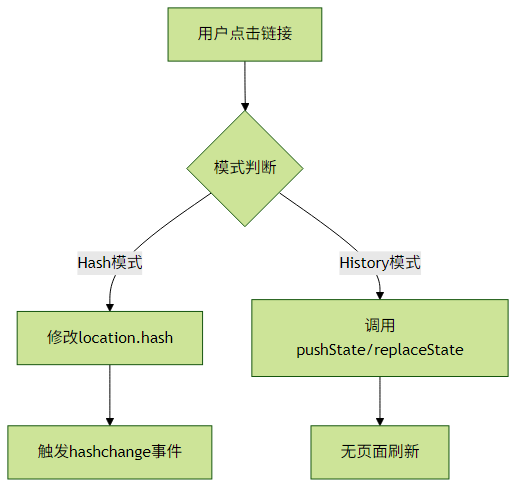
Vue Router提供了两种主要的路由模式,适用于不同的部署环境:
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHashHistory(), // Hash模式
// 或
history: createWebHistory(), // History模式
routes
})Hash模式特点:
- URL中包含
#符号,如http://example.com/#/home - 不需要服务器端配置,适合纯静态部署
- 通过监听
hashchange事件实现路由切换 - 不会发送完整的页面请求到服务器
History模式特点:
- 干净的URL,如
http://example.com/home - 需要服务器端支持(配置回退路由)
- 利用HTML5 History API实现
- 可能遇到404问题,需配置服务器重定向
实践建议:
- 开发环境可使用Hash模式避免配置麻烦
- 生产环境推荐History模式以获得更专业的URL
- 使用History模式时,确保服务器配置了所有路由回退到index.html
Abstract模式
Abstract模式主要用于非浏览器环境,如:
- 服务器端渲染(SSR)
- 移动端原生应用
- 单元测试环境
const router = createRouter({
history: createMemoryHistory(), // Abstract模式
routes
})特点:
- 不会修改浏览器地址栏
- 完全在内存中维护路由状态
- 适合需要路由功能但不依赖URL的环境
二、路由表结构设计
静态路由配置
基础路由配置是一个包含路由记录的数组:
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'Home',
component: HomeView
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'About',
component: () => import('../views/AboutView.vue')
}
]动态路由加载
对于大型应用,可采用路由懒加载优化性能:
const UserDetails = () => import('./views/UserDetails.vue')
const routes = [
{
path: '/users/:id',
component: UserDetails
}
]高级动态加载:可结合权限系统动态生成路由
// 从API获取用户权限路由
async function setupRouter() {
const userRoutes = await fetchUserRoutes()
userRoutes.forEach(route => {
router.addRoute(route)
})
}实践建议:
- 核心路由使用静态配置
- 按功能模块拆分路由文件
- 非核心路由使用动态加载减少初始包大小
- 动态路由考虑添加加载状态和错误处理
三、路由元信息应用
meta字段为路由提供了强大的扩展能力:
const routes = [
{
path: '/admin',
meta: {
requiresAuth: true,
title: '管理后台',
cache: false,
permissions: ['admin']
}
}
]常见元信息用途
权限控制:
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => { if (to.meta.requiresAuth && !isAuthenticated()) { next('/login') } else { next() } })页面标题管理:
router.afterEach((to) => { document.title = to.meta.title || '默认标题' })缓存控制:
<template> <router-view v-slot="{ Component }"> <keep-alive> <component :is="Component" v-if="$route.meta.cache" /> <component :is="Component" v-if="!$route.meta.cache" /> </keep-alive> </router-view> </template>
实践建议:
- 为路由统一设计meta字段规范
- 将权限控制逻辑集中到路由配置中
- 使用TypeScript定义meta类型确保类型安全
- 避免在meta中存储过大或复杂的数据
四、进阶路由设计模式
嵌套路由设计
const routes = [
{
path: '/user/:id',
component: UserLayout,
children: [
{
path: 'profile',
component: UserProfile
},
{
path: 'posts',
component: UserPosts
}
]
}
]命名视图配置
const routes = [
{
path: '/settings',
components: {
default: UserSettings,
helper: SettingsHelper
}
}
]<template>
<router-view />
<router-view name="helper" />
</template>路由滚动行为控制
const router = createRouter({
scrollBehavior(to, from, savedPosition) {
if (savedPosition) {
return savedPosition
} else if (to.hash) {
return {
el: to.hash,
behavior: 'smooth'
}
} else {
return { top: 0 }
}
}
})五、性能优化实践
路由懒加载分组:
const UserDetails = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "user" */ './views/UserDetails.vue')预加载策略:
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => { if (to.meta.preload) { const components = to.matched.map(record => record.components.default) components.forEach(component => { if (typeof component === 'function') { component() } }) } next() })- 路由分割:按功能模块拆分路由配置
六、TypeScript集成
import 'vue-router'
declare module 'vue-router' {
interface RouteMeta {
requiresAuth?: boolean
title?: string
cache?: boolean
permissions?: string[]
}
}
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(),
routes: [
{
path: '/admin',
component: () => import('./AdminView.vue'),
meta: {
requiresAuth: true,
title: 'Admin'
}
}
] as RouteRecordRaw[]
})通过合理配置和设计Vue路由,可以构建出结构清晰、性能优异且易于维护的单页应用。根据项目规模选择合适的路由组织方式,并充分利用路由元信息等高级特性,能够显著提升开发效率和用户体验。
评论已关闭