Vuex测试与调试指南:从单元测试到时间旅行
Vuex 测试与调试完全指南:从单元测试到时间旅行
单元测试 Mutations 和 Actions
为什么需要测试 Vuex?
Vuex 作为 Vue 应用的状态管理核心,其稳定性和可靠性直接影响整个应用。良好的测试可以确保状态变更符合预期,避免难以追踪的 bug。
测试 Mutations
Mutations 是同步修改状态的函数,测试相对简单:
// store/mutations.js
export const mutations = {
increment(state) {
state.count++
},
setValue(state, value) {
state.value = value
}
}
// mutations.spec.js
import { mutations } from './mutations'
describe('mutations', () => {
it('increment should increase count by 1', () => {
const state = { count: 0 }
mutations.increment(state)
expect(state.count).toBe(1)
})
it('setValue should update state.value', () => {
const state = { value: null }
mutations.setValue(state, 'test')
expect(state.value).toBe('test')
})
})实践建议:
- 每个 mutation 应该只做一件事,保持单一职责
- 测试时只需关注输入 state 和 payload 后的输出 state
- 使用对象展开运算符创建测试用的 state 副本,避免测试间污染
测试 Actions
Actions 可能包含异步操作和复杂逻辑,测试需要更多技巧:
// store/actions.js
export const actions = {
async fetchData({ commit }, payload) {
try {
const response = await api.fetch(payload)
commit('setData', response.data)
return response
} catch (error) {
commit('setError', error)
throw error
}
}
}
// actions.spec.js
import { actions } from './actions'
import api from './api'
jest.mock('./api')
describe('actions', () => {
it('fetchData commits data on success', async () => {
const commit = jest.fn()
const mockData = { id: 1, name: 'Test' }
api.fetch.mockResolvedValue({ data: mockData })
await actions.fetchData({ commit }, 1)
expect(commit).toHaveBeenCalledWith('setData', mockData)
expect(api.fetch).toHaveBeenCalledWith(1)
})
it('fetchData commits error on failure', async () => {
const commit = jest.fn()
const mockError = new Error('Failed')
api.fetch.mockRejectedValue(mockError)
await expect(actions.fetchData({ commit }, 1))
.rejects.toThrow(mockError)
expect(commit).toHaveBeenCalledWith('setError', mockError)
})
})实践建议:
- 使用 jest.mock 模拟外部依赖
- 测试成功和失败两种场景
- 验证 commit 是否按预期被调用
- 对于异步操作,确保测试返回 Promise 或使用 async/await
模拟 Store 的测试策略
为什么要模拟 Store?
在组件测试中,我们通常不希望依赖真实的 Store,因为:
- 测试会更复杂且缓慢
- 难以隔离测试组件本身的行为
- 可能导致测试间的状态污染
基本模拟方法
// Component.vue
export default {
computed: {
...mapState(['count']),
...mapGetters(['doubleCount'])
},
methods: {
...mapActions(['increment'])
}
}
// Component.spec.js
import { shallowMount, createLocalVue } from '@vue/test-utils'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import Component from './Component.vue'
const localVue = createLocalVue()
localVue.use(Vuex)
describe('Component', () => {
let store
let actions
beforeEach(() => {
actions = {
increment: jest.fn()
}
store = new Vuex.Store({
state: { count: 1 },
getters: { doubleCount: () => 2 },
actions
})
})
it('renders count and doubleCount', () => {
const wrapper = shallowMount(Component, { store, localVue })
expect(wrapper.text()).toContain('1')
expect(wrapper.text()).toContain('2')
})
it('calls increment action on button click', () => {
const wrapper = shallowMount(Component, { store, localVue })
wrapper.find('button').trigger('click')
expect(actions.increment).toHaveBeenCalled()
})
})高级模拟技巧
对于更复杂的场景,可以使用 createStoreMock 辅助函数:
function createStoreMock(overrides = {}) {
const defaultState = { count: 0, user: null }
const defaultGetters = { isLoggedIn: false }
const defaultActions = { login: jest.fn(), logout: jest.fn() }
return {
state: { ...defaultState, ...overrides.state },
getters: { ...defaultGetters, ...overrides.getters },
mutations: { ...overrides.mutations },
actions: { ...defaultActions, ...overrides.actions },
modules: { ...overrides.modules },
strict: false
}
}
// 使用示例
const store = new Vuex.Store(createStoreMock({
state: { count: 5 },
getters: { isLoggedIn: true }
}))实践建议:
- 为常用模块创建可重用的模拟工厂函数
- 在 beforeEach 中重置模拟状态,确保测试隔离
- 优先测试组件与 store 的交互,而非 store 内部逻辑
- 考虑使用 vuex-mock-store 等库简化流程
开发者工具的时间旅行调试
Vuex 开发者工具简介
Vue Devtools 提供了强大的 Vuex 调试功能,其中最引人注目的是"时间旅行"(Time Travel)调试。

时间旅行调试的核心功能
- 状态快照:记录每个 mutation 后的完整状态
- 回放/前进:跳转到任意历史状态
- 提交/回滚:将状态重置到特定点
- 导入/导出:保存和加载状态快照用于调试
如何使用时间旅行
- 安装 Vue Devtools 浏览器扩展
- 在开发模式下运行应用
- 打开开发者工具 → Vue → Vuex 标签页
- 查看 mutations 时间线
- 点击任意 mutation 跳转到对应状态
实际调试场景示例
假设我们有一个购物车应用,遇到如下问题:
- 添加商品后总价计算不正确
使用时间旅行调试步骤:
- 重现问题:添加几个商品到购物车
- 在 Devtools 中观察每个 ADD_TO_CART mutation 后的状态
- 发现某个 mutation 后计算出现偏差
- 回滚到问题前的状态,检查 payload 和 mutation 逻辑
- 确认是 mutation 中未正确处理商品折扣
实践建议
- 生产环境:确保禁用 Vuex 开发者工具(设置
strict: false) - 性能优化:大型应用中,避免在 mutation 中存储过大状态对象
调试技巧:
- 给 mutation 添加有意义的 type 便于识别
- 对复杂操作使用 action 组合多个 mutation
- 利用"提交状态"功能保存特定场景的快照
- 与测试结合:将 Devtools 导出的状态用于测试用例的初始状态
测试与调试的综合策略
分层测试:
- 单元测试:独立测试每个 mutation 和 action
- 集成测试:测试组件与 store 的交互
- E2E 测试:验证完整流程
- 调试流程:
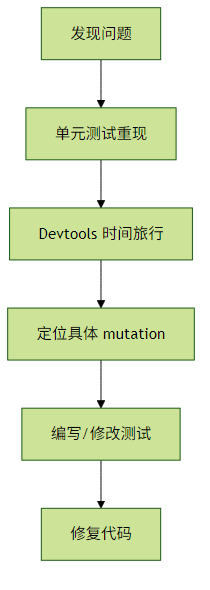
性能考量:
- 测试时避免不必要的 store 创建
- 使用 shallowMount 减少渲染开销
- 对大型 store 考虑模块化测试
通过结合全面的测试策略和强大的开发者工具,可以显著提高 Vuex 代码的质量和可维护性,为复杂应用提供可靠的状态管理保障。
评论已关闭