Vuex与Axios整合及持久化实战指南
Vuex 第三方库深度整合:Axios 与持久化实战指南
一、与 Axios 的深度整合
1.1 为什么需要整合 Axios
在 Vue 应用中,Vuex 负责状态管理,Axios 负责 HTTP 请求,两者结合可以实现前后端数据流的完整闭环。深度整合后可以实现:
- 统一管理 API 请求状态
- 自动触发 Vuex mutations/actions
- 集中处理错误和加载状态
1.2 基础整合模式
最简单的整合方式是在 Vuex actions 中直接调用 Axios:
// store/modules/user.js
actions: {
async fetchUser({ commit }, userId) {
try {
const response = await axios.get(`/api/users/${userId}`)
commit('SET_USER', response.data)
} catch (error) {
commit('SET_ERROR', error.message)
}
}
}1.3 高级封装方案
我们可以创建更优雅的封装:
// utils/api.js
export const createApiService = (axiosInstance, store) => {
return {
async get(url, config = {}, mutation) {
try {
const response = await axiosInstance.get(url, config)
if (mutation) {
store.commit(mutation, response.data)
}
return response
} catch (error) {
store.commit('SET_ERROR', error)
throw error
}
},
// 类似实现 post, put, delete 等方法
}
}
// 在 store 初始化时
const api = createApiService(axios, store)
// 在 actions 中使用
actions: {
async fetchPosts({ commit }) {
await api.get('/posts', {}, 'SET_POSTS')
}
}1.4 请求状态管理最佳实践
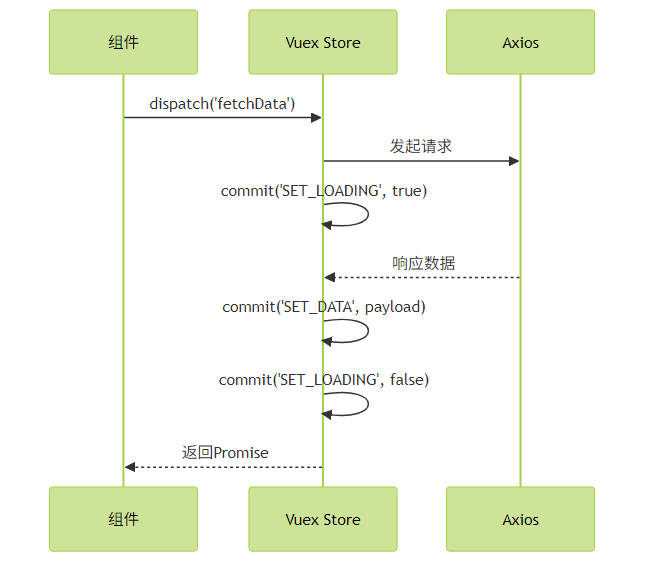
实践建议:
- 为请求状态设计统一的 loading/error 状态结构
- 使用拦截器统一处理 token 和错误
- 考虑使用插件自动生成 API 相关的 Vuex 模块
二、持久化插件 (vuex-persistedstate) 的使用
2.1 为什么需要状态持久化
Vuex 默认是内存存储,页面刷新后状态会丢失。持久化可以:
- 保持用户登录状态
- 记住用户偏好设置
- 实现离线应用的基础
2.2 vuex-persistedstate 基础使用
安装:
npm install vuex-persistedstate基本配置:
import createPersistedState from 'vuex-persistedstate'
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// ...
plugins: [
createPersistedState({
key: 'my-vuex-store', // 存储的键名
paths: ['user', 'settings'], // 只持久化这些模块
storage: window.localStorage // 默认是 localStorage
})
]
})2.3 高级配置选项
createPersistedState({
storage: {
getItem: key => Cookies.get(key),
setItem: (key, value) => Cookies.set(key, value, { expires: 7 }),
removeItem: key => Cookies.remove(key)
},
reducer: (state) => {
return {
user: {
token: state.user.token,
rememberMe: state.user.rememberMe
}
}
},
filter: (mutation) => {
// 只处理特定 mutation
return mutation.type.startsWith('user/')
}
})2.4 安全注意事项
对于敏感数据:
createPersistedState({
paths: ['user'],
storage: {
getItem: (key) => {
const value = localStorage.getItem(key)
return value ? decrypt(value) : null
},
setItem: (key, value) => {
localStorage.setItem(key, encrypt(value))
},
removeItem: (key) => localStorage.removeItem(key)
}
})实践建议:
- 不要持久化敏感信息(如密码)
- 考虑数据加密方案
- 设置合理的过期策略
- 对大型状态考虑使用 IndexedDB
三、综合实战案例
3.1 电商应用状态管理设计
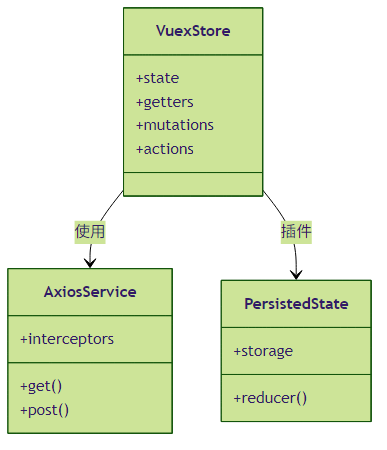
3.2 完整代码示例
// store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import axios from 'axios'
import createPersistedState from 'vuex-persistedstate'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const api = axios.create({
baseURL: process.env.VUE_APP_API_URL,
timeout: 10000
})
// 请求拦截器
api.interceptors.request.use(config => {
const token = store.state.user.token
if (token) {
config.headers.Authorization = `Bearer ${token}`
}
return config
})
// 响应拦截器
api.interceptors.response.use(
response => response,
error => {
if (error.response.status === 401) {
store.commit('user/LOGOUT')
}
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
user: {
namespaced: true,
state: () => ({
token: null,
profile: null
}),
mutations: {
SET_TOKEN(state, token) {
state.token = token
},
SET_PROFILE(state, profile) {
state.profile = profile
},
LOGOUT(state) {
state.token = null
state.profile = null
}
},
actions: {
async login({ commit }, credentials) {
const { data } = await api.post('/login', credentials)
commit('SET_TOKEN', data.token)
commit('SET_PROFILE', data.user)
},
async fetchProfile({ commit }) {
const { data } = await api.get('/profile')
commit('SET_PROFILE', data)
}
}
},
cart: {
state: () => ({
items: []
}),
// ... cart 相关 mutations 和 actions
}
},
plugins: [
createPersistedState({
paths: ['user', 'cart'],
storage: window.sessionStorage, // 使用 sessionStorage 而不是 localStorage
reducer: (state) => ({
user: {
token: state.user.token // 只持久化 token
},
cart: state.cart
})
})
]
})
export default store四、总结与最佳实践
4.1 Axios 整合要点
- 使用拦截器统一处理认证和错误
- 将 API 调用封装在 Vuex actions 中
- 设计良好的请求状态管理结构
4.2 持久化实践建议
- 按需持久化,不要存储整个状态树
- 敏感数据考虑加密或避免持久化
- 根据场景选择 localStorage、sessionStorage 或 Cookies
4.3 性能考量
- 大型状态考虑使用 IndexedDB
- 频繁更新的状态可能不适合持久化
- 使用 reducer 函数控制存储内容
通过合理整合这些第三方库,可以构建出健壮、可维护的 Vuex 状态管理系统,为复杂应用提供坚实的基础架构。
评论已关闭