CSS选择器完全指南:从基础到高级技巧
CSS 选择器深度解析:从基础到高级应用
CSS 选择器是前端开发的基石,掌握它们能让你精准控制页面元素的样式。本文将系统讲解各类选择器的用法,并通过实际案例展示如何高效运用。
一、基础选择器:精准定位的起点
1. 元素选择器
/* 选中所有<p>元素 */
p {
color: #333;
line-height: 1.5;
}2. 类选择器
/* 选中所有class="highlight"的元素 */
.highlight {
background-color: yellow;
font-weight: bold;
}3. ID选择器
/* 选中id="main-header"的元素 */
#main-header {
font-size: 2rem;
border-bottom: 2px solid #000;
}4. 通配符选择器
/* 选中所有元素 */
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}实践建议:
- 优先使用类选择器而非ID选择器,提高样式复用性
- 通配符选择器适合用于全局重置,但要谨慎使用
二、组合选择器:建立元素关系
1. 后代选择器
/* 选中<article>内所有<p>元素 */
article p {
margin-bottom: 1em;
}2. 子元素选择器
/* 只选中直接子元素<ul> */
nav > ul {
list-style-type: none;
}3. 相邻兄弟选择器
/* 选中紧接在<h2>后的<p> */
h2 + p {
margin-top: 0.5em;
}4. 通用兄弟选择器
/* 选中<h3>之后的所有<p> */
h3 ~ p {
color: #666;
}性能优化:
- 避免过长的选择器链(如
body div#main ul li a) - 右对齐原则:浏览器从右向左解析选择器
三、伪类与伪元素:增强交互与装饰
1. 常用伪类
/* 链接状态 */
a:link { color: blue; }
a:visited { color: purple; }
a:hover { text-decoration: underline; }
/* 表单元素 */
input:focus { outline: 2px solid orange; }
input:disabled { opacity: 0.5; }
/* 结构伪类 */
li:nth-child(odd) { background: #f5f5f5; }
tr:nth-of-type(3n) { background: #eef; }2. 伪元素应用
/* 添加装饰内容 */
blockquote::before {
content: "“";
font-size: 3em;
color: #ccc;
}
/* 首字母下沉 */
p::first-letter {
font-size: 2em;
float: left;
margin-right: 0.2em;
}
/* 选中用户选择的文本 */
::selection {
background: #ffeb3b;
color: #000;
}实践案例:创建自定义复选框
.checkbox-container input[type="checkbox"] {
opacity: 0;
position: absolute;
}
.checkbox-container label::before {
content: "";
display: inline-block;
width: 18px;
height: 18px;
border: 2px solid #ccc;
margin-right: 8px;
vertical-align: middle;
}
.checkbox-container input:checked + label::before {
background: #2196F3;
border-color: #2196F3;
background-image: url('checkmark.svg');
background-size: contain;
}四、属性选择器:基于属性的精准匹配
1. 基本属性选择
/* 选中所有有title属性的元素 */
[title] {
border-bottom: 1px dotted #999;
}
/* 选中type="text"的输入框 */
input[type="text"] {
border: 1px solid #ddd;
}2. 高级属性匹配
/* 以"https"开头的链接 */
a[href^="https"]::after {
content: " (安全链接)";
color: green;
}
/* 包含"example"的链接 */
a[href*="example"] {
background: #f0f8ff;
}
/* 以".pdf"结尾的链接 */
a[href$=".pdf"]::before {
content: "📄 ";
}实用技巧:为不同文件类型添加图标
a[href$=".pdf"]::after { content: " [PDF]"; color: #e74c3c; }
a[href$=".doc"]::after { content: " [DOC]"; color: #3498db; }
a[href$=".zip"]::after { content: " [ZIP]"; color: #2ecc71; }五、选择器优先级与最佳实践
1. 优先级计算规则
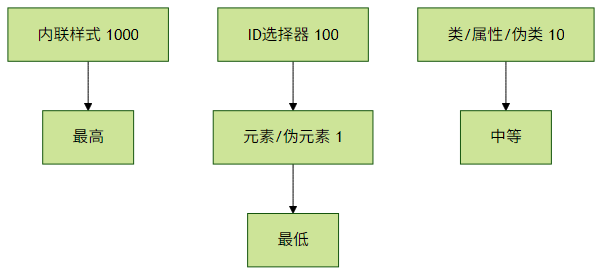
2. 优先级管理技巧
/* 避免过度使用!important */
.button {
background: #2196F3 !important; /* 最后手段 */
}
/* 使用特异性更高的选择器替代!important */
body .special-button {
background: #2196F3; /* 比单独的.button特异性高 */
}3. 现代CSS选择器新特性
/* :is() 简化选择器组 */
:is(h1, h2, h3) {
margin-top: 1.5em;
}
/* :where() 保持低特异性 */
:where(article) p {
line-height: 1.6; /* 特异性为0 */
}
/* :has() 父元素选择(实验性) */
div:has(> .alert) {
border: 1px solid red;
}性能优化建议:
- 避免使用
*选择器作为关键选择器 - 减少使用后代选择器,特别是深层嵌套
- 对频繁变化的元素使用类选择器而非属性选择器
结语
掌握CSS选择器是成为前端高手的必经之路。建议通过以下方式巩固学习:
- 使用浏览器的开发者工具测试选择器
- 定期练习CSS选择器挑战(如CSS Diner游戏)
- 在实际项目中尝试组合使用不同类型的选择器
记住,好的选择器应该像精准的手术刀,既能准确命中目标,又不会影响无关元素。
评论已关闭