Vue国际化实战:动态路由与语言前缀整合指南
Vue国际化实战:动态路由与语言前缀的深度整合
引言
在现代Web应用中,国际化(i18n)已成为必备功能。Vue生态系统提供了强大的国际化支持,但如何优雅地处理多语言路由却是一个常见痛点。本文将深入探讨Vue应用中动态路由的本地化实现,特别是如何处理语言前缀的路由匹配问题。
一、路由路径本地化的核心概念
1.1 什么是路由本地化
路由本地化是指根据用户选择的语言,动态调整应用的路由路径。例如:
- 英文用户访问
/en/home - 中文用户访问
/zh/home - 日文用户访问
/ja/home
这种设计不仅符合SEO最佳实践,还能提升用户体验,让URL结构更直观。
1.2 基本实现原理
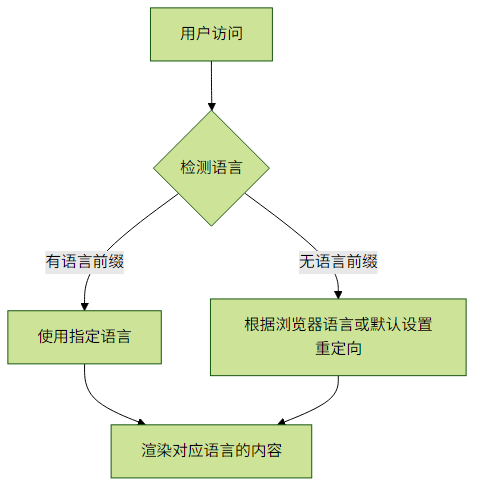
二、实现语言前缀路由匹配
2.1 基础路由配置
首先,我们需要配置Vue Router来处理带语言前缀的路由:
// router.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import Home from './views/Home.vue'
Vue.use(Router)
const router = new Router({
mode: 'history',
routes: [
{
path: '/:lang',
component: {
render(c) { return c('router-view') }
},
children: [
{
path: 'home',
name: 'home',
component: Home
},
// 其他路由...
]
},
// 默认重定向
{
path: '*',
redirect: to => {
const userLang = navigator.language.split('-')[0] || 'en'
return `/${userLang}/home`
}
}
]
})2.2 动态路由生成
对于大型应用,手动编写所有语言路由会很繁琐。我们可以动态生成路由:
// supported-languages.js
export const supportedLanguages = ['en', 'zh', 'ja', 'es']
// router.js
const routes = [
{
path: '/:lang',
component: {
render(c) { return c('router-view') }
},
children: generateRoutes()
}
]
function generateRoutes() {
const baseRoutes = [
{ path: 'home', component: Home },
{ path: 'about', component: About },
// 其他基础路由...
]
return baseRoutes.map(route => ({
...route,
path: route.path,
name: `${route.name}` // 保持名称不变,语言由参数处理
}))
}2.3 路由守卫处理语言切换
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
const lang = to.params.lang
const supportedLangs = ['en', 'zh', 'ja', 'es']
// 如果语言参数无效,重定向到默认语言
if (!supportedLangs.includes(lang)) {
return next(`/en${to.path}`)
}
// 设置i18n语言
i18n.locale = lang
next()
})三、高级路由模式
3.1 混合静态和动态路由
有时我们需要某些路由不受语言影响:
const routes = [
{
path: '/:lang',
component: {
render(c) { return c('router-view') }
},
children: [
// 语言相关路由
{ path: 'home', component: Home },
// ...
]
},
// 语言无关路由
{ path: '/login', component: Login },
{ path: '/api-callback', component: ApiCallback }
]3.2 SEO友好的路由设计
对于SEO,我们可以考虑以下策略:
// 为每种语言创建特定的meta信息
const routes = [
{
path: '/:lang/home',
component: Home,
meta: {
i18n: {
en: { title: 'Home' },
zh: { title: '首页' },
ja: { title: 'ホーム' }
}
}
}
]
// 在全局前置守卫中设置
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
const lang = to.params.lang || 'en'
document.title = to.meta.i18n?.[lang]?.title || 'Default Title'
next()
})四、实践建议
语言检测策略:
- 优先使用URL中的语言参数
- 其次考虑用户上次选择的语言(localStorage)
- 最后回退到浏览器语言
性能优化:
按语言代码分割代码块
const Home = () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "home-[request]" */ `./views/${lang}/Home.vue`)
错误处理:
- 为不存在的语言提供优雅降级方案
- 考虑添加语言选择器组件
开发体验:
- 创建路由生成器工具函数
- 编写单元测试验证路由匹配
五、完整示例
// i18n-router.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import i18n from './i18n'
Vue.use(Router)
const supportedLanguages = ['en', 'zh', 'ja', 'es']
const loadView = (view) => {
return () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "view-[request]" */ `@/views/${view}.vue`)
}
const generateLocalizedRoutes = () => {
const baseRoutes = [
{ path: 'home', name: 'home', component: loadView('Home') },
{ path: 'about', name: 'about', component: loadView('About') },
{ path: 'contact', name: 'contact', component: loadView('Contact') }
]
return baseRoutes
}
const router = new Router({
mode: 'history',
routes: [
{
path: '/:lang',
component: {
render(c) { return c('router-view') }
},
children: generateLocalizedRoutes(),
beforeEnter: (to, from, next) => {
const lang = to.params.lang
if (!supportedLanguages.includes(lang)) {
return next(`/en${to.path}`)
}
next()
}
},
{
path: '*',
redirect: () => {
const storedLang = localStorage.getItem('preferredLang')
const browserLang = navigator.language.split('-')[0]
const lang = storedLang || (supportedLanguages.includes(browserLang) ? browserLang : 'en')
return `/${lang}/home`
}
}
]
})
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
const lang = to.params.lang || 'en'
i18n.locale = lang
localStorage.setItem('preferredLang', lang)
next()
})
export default router六、常见问题解决方案
Q1: 如何处理直接访问根路径的情况?
A: 配置一个通配路由重定向到用户首选语言:
{
path: '/',
redirect: () => {
const lang = detectUserLanguage() // 实现你的语言检测逻辑
return `/${lang}/home`
}
}Q2: 如何保持路由名称简洁?
A: 使用路由元信息扩展而非修改名称:
{
path: 'home',
name: 'home', // 保持名称不变
meta: {
i18n: {
en: { title: 'Home' },
zh: { title: '首页' }
}
}
}Q3: 如何优化语言切换性能?
A: 实现以下策略:
- 预加载目标语言资源
- 使用Webpack魔法注释分割代码
- 实现智能缓存策略
结语
实现Vue中的动态路由本地化需要综合考虑路由结构、用户体验和性能优化。通过本文介绍的技术,你可以构建出既符合国际化标准又保持良好开发体验的Vue应用。记住,良好的路由设计应该对用户透明,让多语言支持成为应用的加分项而非负担。
评论已关闭